Cell
Organ system
Urinary system
Eliminates waste, regulates fluid and electrolyte balance, controls pH.
Digestive system
Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, eliminates waste.
Respiratory system
Exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide, maintains blood pH balance.
Lymphatic system
Defends against infection, maintains fluid balance, absorbs fats.
Cardiovascular system
Circulates blood, nutrients, oxygen, and removes waste
Nervous system
Controls body activities, processes sensory information, plans responses
Muscular system
Allows movement, maintains posture, generates body heat.
Skeletal system
Provides structure, protects organs, stores minerals, allows movement.
Integumentary system
Protects body, controls temperature
Reproduction system
facilitates reproduction, supports fetal development.
Endocrine system
Regulates metabolism, growth, and mood through hormones.
Organsim
Humans
Describes image formed by
Diagram
White light
Gamma Rays
Penetrate human tissues to kill cancer cells
Penetrate human tissue for medical imaging, luggage scanning
Ultraviolet Rays
Produced by Sun and Stars, burn skin and increase risk of cancer, disinfect water
Infrared Waves
Felt as heat, alarms, NVG
Microwaves
Heat food, Radar, mapp the Earth and space objects
Radio Waves
Radio, TV, Cell phones
Waves
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Additive & Subtractive colour theory
Ray Model of Light
Reflection & Refraction
Concave and Convex lenses
SALT
Technical application of lenses and mirrors
The human eye
Convex lenses
Cameras, glasses, telescopes
Type of image
Location
Attitude
Size
Mirrors/lenses
Real images
Light rays actually meet at that point
In Convex lenses, light converges at the focal point to create real images
Virtual images
Light rays only appear to come to that point
In concave lenses, light converges at the focal point to create virtual images
Types of reflections
Diffuse Reflection
All rays are rays are moving in different directions
Specular Reflection
All rays are parallel
Refraction
The bending or change in direction of light when it travels from one substance to another
Index of Refraction
Light moves from a faster substance to a slower substance, the light will bend towards the normal and if the light moves from a slower substance to a faster substance, the light will bend away from the normal
Laws of reflection
Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection
Convex mirrors
Virtual, smaller Images
Divergence rays
Concave mirrors
Real or Virtual images
Focus point
Plane mirrors
Virtual Images
Light and matter interaction
Transmission
Reflection
Light Rays interact in specific ways
Opaque Object
Light rays are reflected
Shadows
Penumbra
The partial shadow part where light rays from a non point source are party blocked
Umbra
Dark areas where all light rays from a source no matter how small or far are blocked
Dark areas where an object blocks direct light rays from a light source
Object far to the source = smaller shadow
Object near to the source = bigger shadow
Translucent Object
Light rays are transmitted and reflected
Transparent Object
Light rays are transmitted
Absoption
This diagram shows how light rays travel in a straight line away from a light source in every direction
Subtractive
When light strikes an object, some waves are reflected and some are absorbed
Coloured matter absorbs different wavelength of light
The absorbed colours "subtracted" from the reflect light
Additive
White like is composed of different colours of light
Violet
Blue
Green
Yellow
Orange
Red
Types of Light
Properties of waves
Frequency
The rate of repetition of a wave
Amplitude
The wave's height or depth from the rest position
Wavelength
Symbol for wavelength is the Greek letter Lambda λ
The distance from one wave to the next
Science Grade 10
Chemistry
Matter
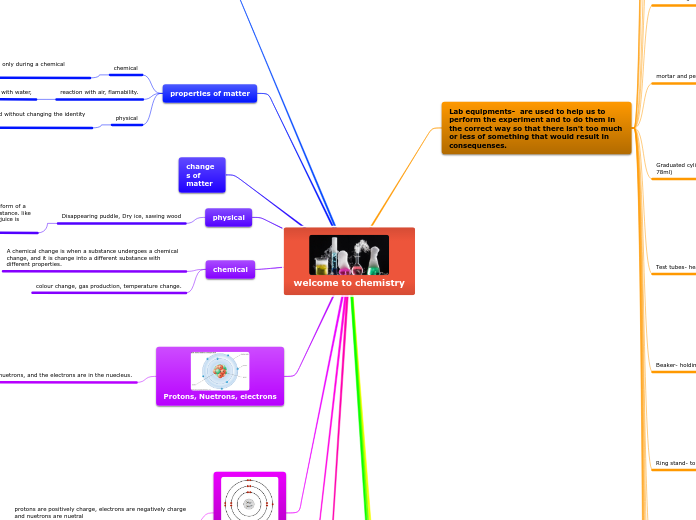
Atomic Structure
Subatomic Particles
Neutrons
A subatomic particle with a neutral charge
Electrons
A subatomic particle with a negative charge
Protons
A subatomic particle with a positive charge
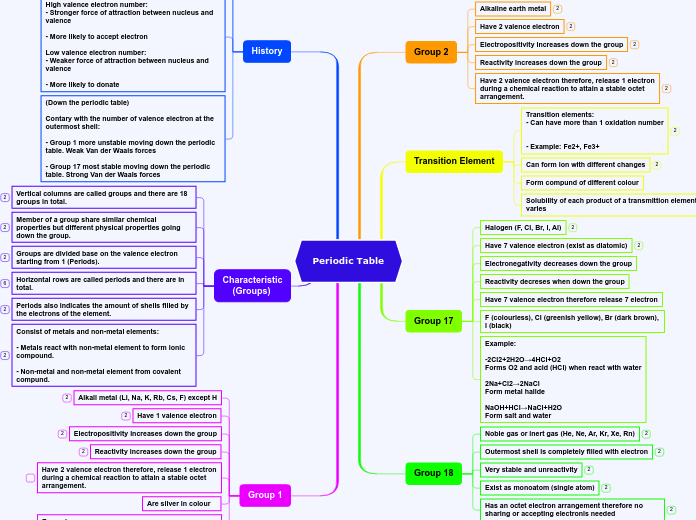
Periodic Table
Element Properties
Metaloids
Nonmetals
Metals
Groups
Noble Gases
Halogens
Alkaline Earth Metals
Alkali Metals
Bohr Diagrams
Chemical Reactions
Neutralization
Acids + base→Salt + Water
Ionic Compounds & Naming
Molecular Compounds & Naming
Counting Atoms
Rules of Counting Atoms
4. A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical symbol and indicates the number of atoms of that element. A coefficient can also be written in front of a chemical formula to indicate the number of molecules of that compound
3 CO2=9 atoms-Carbon-1x3=3
Oxygen-2x3=6
3. A subscript outside a bracket multiplies all the elements inside the brackets
Mg3(PO4)2=13 atoms -Magnesium-3
Phosphorus-2
Oxygen-8
2. A subscript is a number written at the lower right corner after the symbol of an element. If there is more than one atom of the element, then a subscript is used to indicate the number of atoms of that element
H2SO4=7 atoms - Hydrogen-2
Sulfur-1
Oxygen-4
1. The symbol of an element represents one atom of that element
NaCl= 2 atoms - Sodium-1
Chlorine-1
Law of Conservation Mass
Word equations
Acids & Bases
Usually ends with "OH" or "CO3"
ionic compounds
Metal oxides
Slippery like soap
Bitter like tonic water
A substance that produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water
Acids
Usually begins with "H"
Molecular compounds
Non-metal oxides
Good conductors of electricity
Like water
Sour such as lemons, vinegar
A substance that produces hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
Just like chemical equations only the elements in word form
Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Polyatomic Ions
Transition Metals
Examples
Tempature Change
Gas Production
Color Change
Combustion
When all substances in a compound are combined with oxygen
Double Displacement
AB + CD → AD + CB
Single Displacement
A + BC → AC + B
Decompostion
AB → A + B
Synthesis
A + B →AB
States of matter
Gas
Solid
Liquid
Physics
The Wave Model of Light
-When light passes through a prism, it separates into the colours of the rainbow
Biology
Microscopes
Magnifys objects that are to small to be seen with the naked eye
Cells
Animal Cells
Mitochondria
Power house of the cell
Plant Cells
Chloroplasts
Produce energy from photosynthesis
Cell Walls
Provides structural strength
The Cell Cycle
Specialised Cells
Tissues
Hierarchy of organization
Interdependent organs
Medical Imaging Technologies
X-Rays
Uses radiation to capture images of bones and organs.
PET-Scan
Detects radioactive tracers to observe metabolic activity in tissues.
Ultrasound
Uses sound waves to produce images of soft tissues and organs.
CT-Scan
Combines X-ray images for detailed cross-sectional views of the body.
Medical Resonance Imaging
Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed body images.
Interdependent organs work together to maintain body functions
Skeletal and muscular system
Muscles move bones for body movement and posture.
Lungs and diaphragm
Diaphragm controls lung expansion for breathing and oxygen intake.
Endocrine and
reproductive system
Hormones from endocrine glands regulate reproduction and development.
Skin and circulatory system
Skin regulates temperature, circulatory system delivers nutrients to skin.
Eye and brain
Eyes collect visual information, brain processes and interprets it.
Pancreas and small intestine
Pancreas secretes enzymes to aid digestion in small intestine.
Liver and Digestive system
Liver processes nutrients from food for digestion and absorption.
Kidneys and Bladder
Kidneys filter waste, bladder stores urine for excretion.
Brain and Muscles
Brain sends signals to muscles for movement and coordination
Heart and Lungs
Heart pumps blood, lung help for circulation.
Plant cells
Meristematic
Ground
Epidermal
Vascular
Animal tissues
Muscle
Moves the body or organ by contracting
Connective
Strengthens, supports and protects other tissues.
Epithelial
Lines the outer surface of internal organs
Plant Specialized Cells
Phloem
Responsible for
transporting sugar
Xlyem Cells
Responsible for transporting
water and dissolved minerals
Animal specialized cells
White Blood Cells
A cell that protects you from diseases.
Red Blood Cells
Carries oxygen through the blood
Muscle Cells
Contracts allowing bones to move.
Stem Cells
Embryonic cells
Cancer
Mitosis
Telophase
Nuclear membrane reform to form new nuclei
Anaphase
The sister chromatids are pulled a part by the spindle fibers.
Metaphase
The chromosomes become complletely condensed
Prophase
First part of mitosis where the nuclear membran dissolves and disappears