Unit 2 Chemistry notes
Main topic
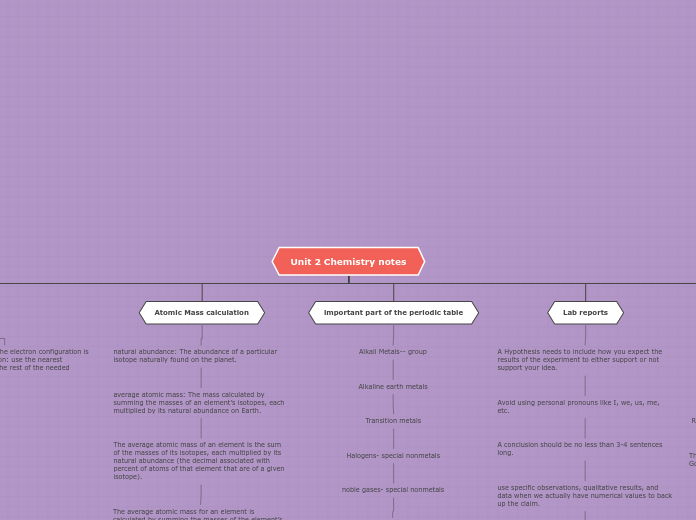
Atomic mass
The atomic mass of an element that you see on the
periodic table is a weighted average of all the isotopes of
an element in the known world.
It is a statistical average, so we calculate it differently
Isotopes
Atoms with the same element but have different masses
They have the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons, adding neutrons will make the atom heavier though will not totally change the chemistry of the atom
Atoms
The fundamental building block of matter, and still possesses the properties of their element
Proton: positive charge, same mass as a neutron, found in the nucleus, Atomic number is the number of protons, attracted to electrons.
Electrons: negative charge, found in energy levels/ electron cloud outside the nucleus, almost zero mass (0.0005 amu), attracted to proton, (a neutral atom is made up of the same number of protons and electrons
Neutron: Zero charge because it is a proton and a neutron put together, found in the nucleus, about the same mass as a proton (1 amu), separates protons, need to d the maths do find the number of neutrons.
atomic number
Determines the number of protons an atoms has
Determines the identity of the element.
Represented by whole numbers of the periodic table
The atomic mass can be written in this manner: Gold-!97
Lab reports
A Hypothesis needs to include how you expect the results of the experiment to either support or not support your idea.
Avoid using personal pronouns like I, we, us, me, etc.
A conclusion should be no less than 3-4 sentences long.
use specific observations, qualitative results, and data when we actually have numerical values to back up the claim.
If... (independent variable) then.... (dependent variable) because of ....(your prior experience knowledge).
important part of the periodic table
Alkali Metals-- group
Alkaline earth metals
Transition metals
Halogens- special nonmetals
noble gases- special nonmetals
The main way elements are categorized as metal, nonmetals, metalloids.
Subtopic
Atomic Mass calculation
natural abundance: The abundance of a particular isotope naturally found on the planet.
average atomic mass: The mass calculated by summing the masses of an element’s isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance on Earth.
The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the masses of its isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance (the decimal associated with percent of atoms of that element that are of a given isotope).
The average atomic mass for an element is calculated by summing the masses of the element’s isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance on Earth.
Electron configuration
a shorter way of writing the electron configuration is the noble gas configuration: use the nearest previous noble gas with the rest of the needed configuration.
Rules that apply
Pauli's exclusion Principle: Two electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
Hund's Rule: when filling up a sub level, all orbitals must first be filled before doubling up electrons in the same orbital
Aufbau principle: Electrons begin filling up the lower energy levels before filling up the higher energy levels.
The types of orbitals
P Orbital will be bigger than the s orbital
SPDF
Highest energy levels contain the electron valences
find the number of electron valences using the group number
An orbital is where an electron can be located at any given moment
pauli's exclusion principle: Two electrons in the same orbital must have opposite sins
a shorter way of writing the electron configuration is