arabera Kanyanat wawsawad 9 years ago
1417
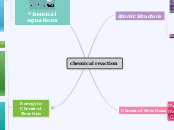
chemical reaction
arabera Kanyanat wawsawad 9 years ago
1417

Honelako gehiago
Energy Change During ReactionsDuring chemical reactions old bonds are broken and new bonds are made.
-Energy can be taken in from the surrounding.
- Energy can be given out to the surrounding.This energy can be in forms of:
- Heat
- Light
- Sound
- Electricity
Reactant - chemicals that start the reactant
Product - chemicals produced by the reaction
Conclusion:metal oxide + acid = salt + water -metal hydroxide + acid = salt + water -metal carbonate + acid = salt + water + carbon dioxide -