arabera Emma Joseph 3 years ago
276
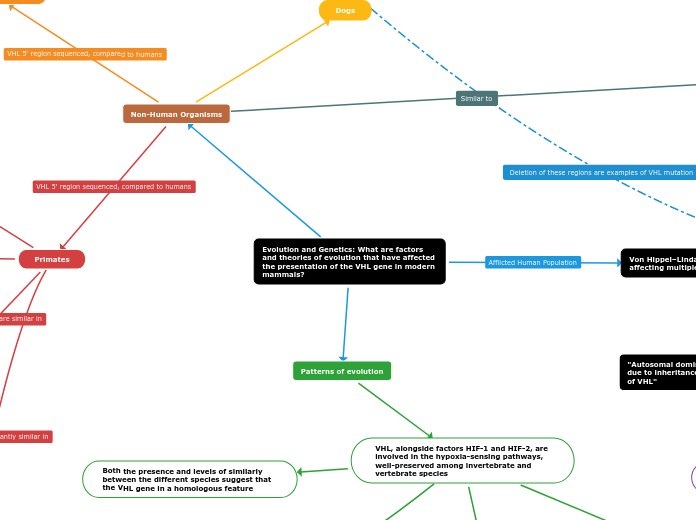
Evolution and Genetics: What are factors and theories of evolution that have affected the presentation of the VHL gene in modern mammals?
arabera Emma Joseph 3 years ago
276

Honelako gehiago
Environmental
Physical factors
Chemical exposure
Chance errors in cell replication
P192A and L188V mutations in one allele, “polycythemia-causing” p.R200W in the second allele
Appears during the formation of gametes or in early stages of the zygote
Associated with worse prognoses/higher rates of fatal cysts and tumors
Truncating
Most destructive in the Sp 1 region
Frameshift
In-frame
In exons
Deletion and certain missense mutations result in an increased risk for hemangioblastoma and RCC formation
Named von Hippel Lindau in 1960
VHL gene was identified in 1993
Arvid Lindau
1923-1926: Got his PhD studying CNS tumor and cyst pathology
Eugen von Hippel
1911: Named the disease "angiomatosis retinae"
1904: First described rare disorder in the retina
However, each variation is associated with different increased probability of presenting certain tumors/cysts depending on depending which VHL type, which cell type, and the second mutation location
Type 2
Type 2C - No risk for renal cell carcinoma
Type 2B - High risk for renal cell carcinoma
Type 2A - Low risk for renal cell carcinoma
Type 1
Genetic Hallmarks
Cysts
Tumors
Dog oncogenesis differs
Lower prevalence of VHL mutations
Sequence conservation over 100 million years of evolution highlights evolutionarily conserved regions; When removed, testing showed a reduction in function of the VHL gene
Four evolutionarily conserved regions were identified; Nucleotide identity similarity above 65%
Region 2: Between nucleotides −49 to −19
Region 1: Between nucleotides +2 to +17
Entire VHL 5‘ sequence: 93% similarity
106 bp minimal promoter region: 95% similarity
Diverged from primates earlier
Entire VHL 5‘ sequence: 45% similarity
106 bp minimal promoter region: 50% similarity
Entire VHL 5‘ sequence: 96% similarity
106 bp minimal promoter region: 97% similarity
Diverged from humans last
Entire VHL 5‘ sequence: 98% similarity
106 bp minimal promoter region: 99% similarity
"Variations in the VHL gene within different species is a result of divergent evolution, triggered by animals first diversifying between 600 and 500 million years ago under conditions that today would be described as hypoxic"
Combinations of VHL Phen+3 and HIF1α Metn-3 emerged during evolution through multiple lineages
Emerged approximately 500 million years ago in the modern-day lampreys' ancestors
Substitutions resulted in functional divergence
Specialized hypoxic signalling relative to vertebrate needs/oxygen consumption
VHL affinity to HIFa genes
HIFα-VHL complex stability varies between species and drives adaptation to their environments
Significant variation is tolerated due to unique selective pressures
Example: HIF1α Metn-3 is the most stable HIFα-VHL complex, present in many animals
Humans have three HIFα proteins
HIF3α
HIF2α
HIF1α
Most tightly bonded to VHL
Example: HIFα Metn-3
Primary gene present in sequence analysis of metazoan oxygen-sensing species
Present in the last common ancestor to lophotrochozoa and ecdysozoa species
Diverged in the ecdysozoa
Larger evolutionary divergence due to lower VHL affinity
Core proteins critical for oxygen-sensing)
Creation of (negative regulator) pVHL
Created the secondary contact between HIF1α Met561 and VHL Phe91 sequences