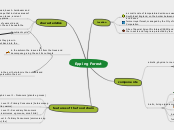
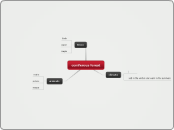
Epping Forest
features of the food chain
Trophic Level 4 - Tertiary Consumers (omnivores eg
badger, owl, fox)
Trophic Level 3 - Secondary Consumers (smaller
carnivores eg mouse, small bird)
Trophic Level 2 - Primary Consumers (herbivores
eg caterpillar, worms)
Trophic Level 1 - Producers (plants eg moss)
characteristics
nutrient cycle
in the autumn the leaves fall from the trees and decompose,
giving the soil its nutrients
earth worms in the soil help to mix the nutrients
and blend the layers within the soil
the tree roots are deep so help to break up the rock
below. this helps to give the soil more nutrients
the trees take up nutrients in the soil as they grow in summer. However, more nutrients are put back into the soil in autumn
Many of the trees are hundreds of years old and support many insects and fungi. the soil beneath the forest is a fertile brown earth
Broad leaf trees such as oak, beech. hornbeam
and elm. It has diverse landscape that includes areas
of historic wood, pasture, green lanes, ancient pollarded
trees and grassy plains
components
biotic, living
organisms
fungi
bacteria
humans
animals
plants
abiotic, physical or non
living organisms
nutrients in the soil
rocks
pH
wind, carbon dioxide, oxygen
water
light
temperature, humidity
location
Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and many of the insects and fungi are protected by law
former royal forest, managed by the City of London Corporation
a small scale of temperature deciduous woodland in South-
East England, on the border between London and Essex