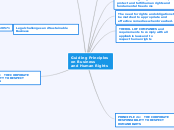
Operational principles
General principles
Carlos Hernandez Torres 201320571
Legal challenges and Sustainable Business
Guiding Principles
on Business
and Human Rights
PRINCIPLE 2.0: THE CORPORATE RESPONSIBILITY TO RESPECT
HUMAN RIGHTS
Processes to enable the remediation of any adverse human rights impacts they cause or to which they contribute.
issues of context
Treat the risk of causing or contributing to Gross human rights abuses.
Seek ways to honor the principles when faced conflicting requirements
Prioritize actions to address potential Human rights impacts before they could become irremediable.
Comply with laws and respect international HR
All enterprises regardless of their Size, sector, operational context,have to respect human rights.
ownership and structure.
To respect human rights refers to internationally recognized human rights : this includes to avoid ANY causing or contributing to adverse human rights impacts
through their OWN ACTIVITIES.
Avoid Infringing on the human rights of others and third parties.
COMPANIES MUST
PRINCIPLE 1: THE STATE DUTY TO PROTECT HUMAN RIGHTS
Ensuring policy coherence
Should ensure that governmental departments, agencies and
other State based institutions that shape business practices are aware
of and observe the State’s human rights obligations when fulfilling
their respective mandates
Encourage, and where appropriate require, business enterprises to communicate how they address their human rights impacts
Promote respect for human rights by business enterprises
with which they conduct commercial transactions.
HUMAN RIGHTS IN CONFLICT AREAS
PROVIDE ASSISTANCE TO ASESS LEGISLATIONS AND REGULATIONS TO ENFORCE MEASURE HR RISK.
DUE TO PROTECT STATE SHOULD
Provide and encourage an effective guidance to enterprise on how to respect HR and address impacts.
ENFORCE AND ENSURE THE DUTIES THAT AIMED TO ENTERPRISE TO RESPECT HR.
OBLIGATIONS TO PROTECT HUMAN RIGHTS
PRINCIPLE 2.1: THE CORPORATE RESPONSIBILITY TO RESPECT
HUMAN RIGHTS
Remediation
IF Business identify that they have caused or
contributed to adverse impacts, they should provide for or cooperate in
their remediation through legitimate processes.
HUMAN RIGHTS DUE DILIGENCE
Effective integration requires that:
Responsibility for addressing such impacts is assigned to the
appropriate level and function within the business
TO ADRESSES HR IMPACTS
Provide information that is sufficient to evaluate the adequacy of
an enterprise’s response to the particular human rights impact
involved
Be based on appropriate qualitative and quantitative indicators
The business if causes or contributes to an
adverse impact, or whether it is involved solely because the
impact is directly linked to its operations
Involve meaningful consultation with potentially affected groups
and other relevant stakeholders
PREVENT, MITIGATE AND COMPENSATE
Recognizing that the human rights risks may
change over time as the business enterprise’s operations and
operating context evolve
IDENTIFY HR RISK INTEGRATE, INTERNATIONAL LAW STANDARDS.
TRACK RESPONSE COMMUNICATE (INTERNALLY AND EXTERNALLY )
OPERATIONAL PRINCIPLES
is approved by the senior level of business enterprise, informed by expertise stipulates HR expectations of personnel partners and operations, finally is reflected in procedures
Is reflected in operational policies and procedures necessary to
embed it throughout the business enterprise.
Is publicly available and communicated internally and externally.
to all personnel,
Stipulates the enterprise’s human rights expectations of personnel,
business partners and other parties directly linked to its operations
Is informed by relevant internal and/or external expertise.
Basis for embedding their responsibility to respect human rights,
business enterprises should express their commitment to meet this
responsibility through a statement of policy
ADDITIONALLY THE COMPANY MUST have in place policies and processes appropriate to
their size and circumstances
THE ROLL OF COMPANIES and requirements to comply with all applicable laws and to
respect human rights
The need for rights and obligations to be matched to appropriate and
effective remedies when breached.
States’ existing obligations to respect, protect and fulfil human rights and
fundamental freedoms
PRINCIPLE 3: ACCESS TO REMEDY
OPERATIONAL PRINCIPLE
Companies should consider ways to facilitate access to effective non State based
grievance mechanisms dealing with business-related human
rights harms
Company Business should participate
in effective operational level grievance mechanisms for individuals and communities who may be adversely impacted
Companies should provide effective and appropriate non-judicial grievance
mechanisms, alongside judicial mechanisms,
Effectiveness criteria for non judicial grievance mechanism.
Collaborative initiatives should ensure the availability of effective mechanism.
the mechanism prevent harms from compounding and grievances from escalating.
Support directly impacted by analyzing practices
states should take aproppiate steps to ensure rthe effectiveness of domestic judicial mecanism.
reduce legal practical and other relevant barriers
those barriers could lead to a denial access to remedy
Access to the effective Remedy
As a part of state duty to protect against business related human rights abuse the must take appropriate steps to ensure.
REMDIATION
Enterprise identify their adverse impacts and should cooperate in remediation through legitimate process.