Math 104
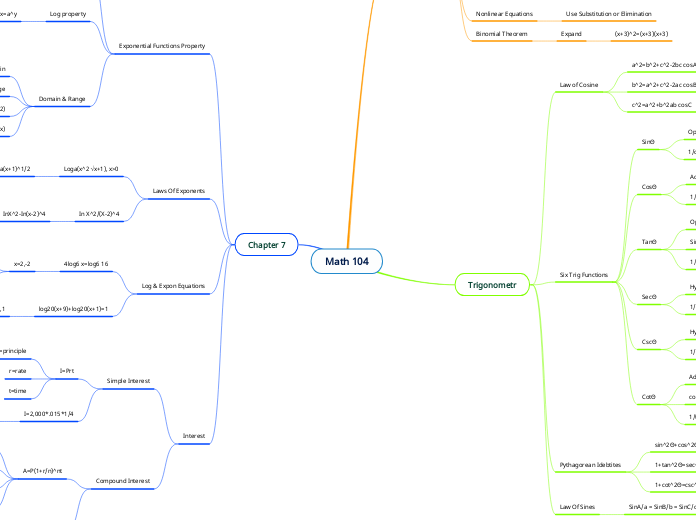
Chapter 7
Interest
Compound Interest
A=2,000(1+(0.015/4)^4*1
A=$2030.17
A=P(1+r/n)^nt
n=times it compound
Simple Interest
I=2,000*.015*1/4
I=$2038.17
I=Prt
t=time
r=rate
P=principle
Log & Expon Equations
log20(x+9)+log20(x+1)=1
X=-1,1
Final answer: x=1
4log6 x=log6 16
x=2,-2
Final Answer: x=2
"x cant be negative"
Laws Of Exponents
In X^2/(X-2)^4
InX^2-In(x-2)^4
"Express all powers as factors"
2Inx-4In(x-2)
Loga(x^2 √x+1), x>0
2logax+loga(x+1)^1/2
"Express All powers as factors"
All powers= Exponents
2logax+1/2loga(x+1)
Exponential Functions Property
Domain & Range
g(x)=log(5+x/5-x)
Interval Notation: (-5,5)
f(x)=log3(x+2)
Domain: {x|X>-2}
Interval Notation: (-2,∞)
Range
(∞,∞)
Domain
(0,∞)
Cant have zero so its not included
Log property
y=logx ↔ x=a^y
log3 81 ↔ y=log3 81
y=4
e^u=25 ↔ u=loge25
1.6^3= ↔ 3=log1.6
y=log7x ↔ x=7^y
a^u=a^v ↔ u=v
Trigonometr
Law Of Sines
SinA/a = SinB/b = SinC/c
Pythagorean Idebtites
1+cot^2Θ=csc^2Θ
1+tan^2Θ=sec^2Θ
sin^2Θ+cos^2Θ=1
Six Trig Functions
CotΘ
1/tanΘ
cosΘ/sinΘ
Adjacent/Opposite
CscΘ
1/sinΘ
Hypotenuse/Opposite
SecΘ
1/cosΘ
Hypotenuse/Adjacent
TanΘ
1/cotΘ
SinΘ/cosΘ
Opposite/Adjacent
CosΘ
1/secΘ
Adjacent/ Hypotenuse
SinΘ
1/cscΘ
Opposite/Hypotenuse
Law of Cosine
c^2=a^2+b^2ab cosC
b^2=a^2+c^2-2ac cosB
a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc cosA
Chapter8
Binomial Theorem
Expand
(x+3)^2=(x+3)(x+3)
Nonlinear Equations
Use Substitution or Elimination
Determinants
Cramer's Rules
3x3 Determinants
2x2 Determinats
Matrices
Row Echelon Form
Augmented Matrix
Systems Of Equations
Consistent, Inconsistent, And Dependent