arabera José Miguel Perales Vaquera 4 years ago
282
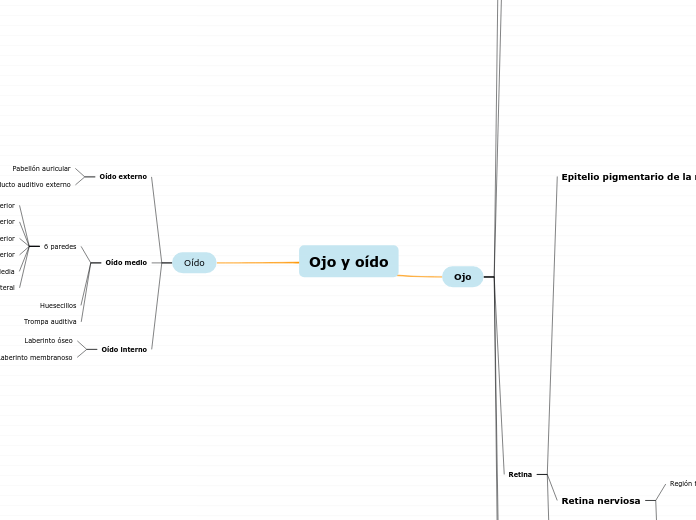
Ojo y oído
arabera José Miguel Perales Vaquera 4 years ago
282

Honelako gehiago
Rivers have always been essential for human life and settlement. A source for drinking, the source of food, and a way to transfer goods from one place to another. They are essential in the environment of rainforest and wetlands.
Lateral
Media
Posterior
Anterior
Inferior
Superior
Varios lóbulos individuales de adenómeros tubuloacinares serosos Hay células epiteliales y mioepiteliales Salen al fornix conjunctival a través de conductos excretores
Llegan a conductivos lagrimales
Después forman conducto nasolagrimal
Revestidos por epitelio seudoestratificado ciliado
Pelos cortos y rígidos ubicados en borde anterior del margen del párpado
Compuesta por
Glándulas lagrimales accesorias
Tubuloalveolares compuestas serosas
Glándulas apócrifas de las pestañas (de Moll)
Glándulas sebaceas de las pestañas (Zeis)
Glándulas tarsales (de Meibomio)
25 en párpado superior 20 párpado inferior
Sudoríparas largas
Glándulas sudoríparas ecrinas
Piel Tarso (tejido fibroso y elastico) Músculo tarsal superior Músculo orbicular del ojo
Membrana mucosa Reviste esclera y cornea y cara posterior de párpados
Epitelio cilindrico estratificado Células caliciformes
Compuesto por Agua glucosaminoglucanos Colágeno Hialocitos
Fibras del cristalino
Subtopic
Epitelio subcapsular
Presentes solo en cara anterior Son cubicas En ecuador migran a cara posterior y se convierten en c. fibrosas del cristalino
Cápsula del cristalino
Lámina basal
Compuesta por Colágeno tipo IV Elastina proteoglucanos
The Volga is the longest river in Europe. The waters of the Volga are used to irrigate the steppe regions of southern Russia. Because of its importance in the country, the Volga has mythological status in Russia, and many iconic sites are found along its banks
The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe. Travelers can experience many of the river's sights by embarking on a cruise along its waterways. Danube River Cruises, which are offered by Viking Cruises, typically stop in Cologne, Budapest, Nuremberg, Belgrade and Krems. Following the river is a way to experience several Eastern European cities in one trip. Famous monuments, such as the Hungarian Parliament, have been erected on its coast.
5 capas internas son irrigadas por A. retiniana
1 capas externas se nutren por difusión desde la coroides
The Volga is the longest river in Europe with a catchment area of 1,350,000 square km.
Eleven of the twenty largest cities of Russia, including the capital, Moscow, are located in the Volga's drainage basin. Rising in the Valdai Hills 225 meters above sea level northwest of Moscow and about 320 km southeast of Saint Petersburg, the Volga heads east past Lake Sterzh, Tver, Dubna, Rybinsk, Yaroslavl, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. From there it turns south, flows past Ulyanovsk, Tolyatti, Samara, Saratov, and Volgograd, and discharges into the Caspian Sea.
Tributaries: Kama, Oka, Vetluga, and Sura. The Volga Delta has a length of about 160 kilometers and includes as many as 500 channels and smaller rivers.
Región no fotosensible (Véase túnica media)
Volga River has 23 main tributaries. Type in several examples.
Situada por delante de la ora serrana Cubre superficie posterior de cuerpo ciliar y cara posterior de iris
Región fotosensible
Presenta 10 capas
Membrana limitante interna
Lámina basal de células de Müller
Capa de fibras del nervio óptico
Formada por evaginaciones que salen de c. Ganglionares y se dirigen hacia el cerebro
Capa ganglionar
Núcleos de c. Ganglionares
Capa plexiforme interna
Evaginaciones de C. Horizontales, bipolares, amacrinas, y ganglionares
Capa nuclear interna
Cuerpos nucleares de c. De Müller, amacrinas, bipolares y horizontales
Capa plexiforme externa
Contiene evaginaciones de los conos y bastones y de las c. Horizontales, amacrinas y n. Bipolares
Capa nuclear externa
Contiene cuerpos nucleares de c. Fotoreceptoras
Membrana limitante externa
Límite apical de c. De Müller
Conos y bastones
Contiene segmentos externo e interno de c. Fotoreceptoras
Epitelio pigmentario
Capa más externa, unidas a membrana de Bruch
4 tipos de células
C. De sostén
Astrocitos
Microglia
C. De Müller
Forman armazón para toda la retina
Neuronas de asociación
C. Amacrinas
Realizan interconexión compleja con c. Bipolares, ganglionares, interplexiformes, otras c. Amacrinas
C. Interflexiformes
Sinapsis entre capa plexiforme externa e interna
C. Centrífugas
C. Horizontales
Sinapsis con las esféricas de los bastones, los pedículos de los conos y c. Bipolares
Neuronas de conducción
C. Ganglionares
C. Bipolares
Establecen sinapsis con C. Ganglionares
C. Fotocensibles
Bastones
Sensibles a la luz (Blanco y negro)
120 millones
Conos
3 tipos
S
Longitud de onda corta (Azul)
M
Longitud de onda media (Verde)
L
Longitud de onda larga (Rojo)
7 millones
The Danube is located in Central and Eastern Europe.
The Danube flows through 10 countries, more than any other river in the world. Originating in the Black Forest in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for 2,850 km, passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. The mouth of the Danube is the Danube Delta. The greater part of the Danube Delta lies in Romania, with a small part in Ukraine (Odessa Oblast).
Tributaries :Iller, Lech, Altmühl, Naab, Regen, Isar, Inn, Ilz, Enns, Morava, Rába, Váh, Hron, Ipeľ, Sió, Dráva, Vuka, Tisza, Sava, Tamiš, Great Morava, Mlava, Karaş, Jiu, Iskar, Olt, Osam, Argeș, Ialomița, Siret, Prut.
Sus funciones son
Remember that this is the original point from which the river flows. Type in the answer.
Fagocitosis y eliminación de discos membranosos
Restauración de fotosencibilidad
Formar barrera hematoretiniana
Absorción de la luz
Posee extensiones que rodean las evaginaciones de conos y bastones
Coroides
The Yangtze or Yangzi is the longest river in Asia and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country (Qinghai, Tibet, Yunnan, Sichuan, Chongqing, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Anhui, Jiangsu, Shanghai provinces). It rises in the northern part of the Tibetan Plateau and flows 6,300 km in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea.
Tributaries: Yalong, Min, Tuo, Jialing, Han, Wu, Yuan, Zi, Xiang, Gan, Huangpu.
In mid-2014, the Chinese government announced it was building a multi-tier transport network, comprising railways, roads, and airports, to create a new economic belt alongside the river.
Se distinguen dos capas
Membrana de Bruch
Se identifican 5 capas
Membrana basal para células de la retina
Capa de fibras de colágeno
Capa de fibras elásticas
Capa de fibras colágenas
Lamina basal de la capa coriocapilar
Se extiende desde el nervio óptico hasta la ora serrana
Se encuentra entre la capa coriocapilar y la retina
Capa coriocapilar
Provee sustancias nutritivas a las células de la retina
Posee capilares fenestrados
Cuerpo ciliar
The Mekong is a trans-boundary river in Southeast Asia. Its estimated length is 4,350 km.
From the Tibetan Plateau, the river runs through China's Yunnan Province, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam.
The Mekong rises as the Za Qu and soon becomes known as the Lancang (Lantsang) in the 'Three Rivers Source Area' on the Tibetan Plateau in the Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve. It approaches and empties into the sea through the Mekong Delta. Tributaries: Nam Khan, Tha, Nam Ou, Mun, Tonle Sap, Kok, Ruak.
Epitelio
Mekong River has many tributaries. Type in at least 3 of its affluents.
Continuación directa da las dos capas de la retina e iris
Where is the place where Mekong drains into a larger body of water ? Type in the answer.
Región vascular interna
Presenta procesos ciliares
3 Funciones principales
Síntesis de fibras zonulares que fijan cristalino
Participación en barrera hematoacuosa
Secreción de humor acuoso
Revestidos por dos capas de epitelio
Capa pigmentaria Su lámina basal se comunica con el estroma vascular
Capa no pigmentaria Su lámina basal se encuentra en contacto con la cámara posterior y la cámara vitrea
Músculo ciliar Se origina en espolón escleral
Porción circular
Reducen tensión sobre el cristalino
Porción radial
Se insertan en cuerpo ciliar (aplanar cristalino)
Porción meridional
Se dirigen al estroma de la coroides
Iris
Formado de anterior a posterior por
En su centro se encuentra la pupila
Células pigmentarias posteriores
Células mioepiteliales pigmentarias anteriores
Son continuación de la retina
M. Dilatador de la pupila
Músculo liso
M. Esfínter de la pupila
Estroma de T.C. Incluye melanocitos
There are four major rivers in Africa: the Nile, the Zambezi, the Congo, and the Niger. The Nile is one of the longest rivers in the world.
The Zambezi's most noted feature is Victoria Falls. Other notable falls include the Chavuma Falls at the border between Zambia and Angola, and Ngonye Falls, near Sioma in Western Zambia.
The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. The area of its basin is 1,390,000 square km.
The 2,574-km-long river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.
Major tributaries: Chifumage River, Luena River, Kabompo River, Lungwebungu River, Luanginga River, Gwayi River, Sengwa River, Sanyati River, Kafue River, Luangwa River, Panhane River, Luia River.
Se puede dividir en
Lámina supracoroides
Fibras colágenas delgadas, Fibras elásticas, fibroblastos, melanócitos, macrófagos
En contacto con coloides
sustancia propia (Cápsula de Tenon)
Inserción de músculos extrínsecos
Fibras colágenas gruesas
Lámina epiescleral
T.C.L. contiguo al T. adiposo
Fibroblastos
Sustancia fundamental
The Zambezi has numerous tributaries. Type is some of its major affluents.
Fibras elásticas
Where is the place where Zambezi drains into a larger body of water ? Type in the answer.
Fibras de colágeno
Try to state the length either in miles or in kilometers.
The Nile, which is about 6,650 km long, covers eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan and Egypt.
It has two major tributaries, the White Nile and the Blue Nile. The White Nile is the headwaters and primary stream of the Nile. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, with the most distant source still undetermined but located in either Rwanda or Burundi. The two rivers meet just north of the Sudanese capital of Khartoum.
The northern section of the river flows north almost entirely through the Sudanese desert to Egypt, then ends in a large delta and flows into the Mediterranean Sea.
Limbo esclerocorneal
Ángulo iridocorneal
Conducto de Schlemm
Drenan humor acuoso
Células madre corneolimbales
Limite entre esclera y córnea
Compuesta por 5 capas
The Nile flows through 7 countries and 3 republics from Africa. Type them in.
Endotelio plano simple
Forma pared anterior de Cámara anterior
Membrana de Descemet
Membrana basal posterior
Estroma
Fibroblastos aplanados y finos
Proteoglucanos corneales
Laminillas colágenas dispuestas ortogonalmente
Membrana de Bowman
Membrana basal anterior
Epitelio plano estratificado
5 capas