arabera Angel Barrera 10 years ago
5271
Simple Past VS Present Perfect
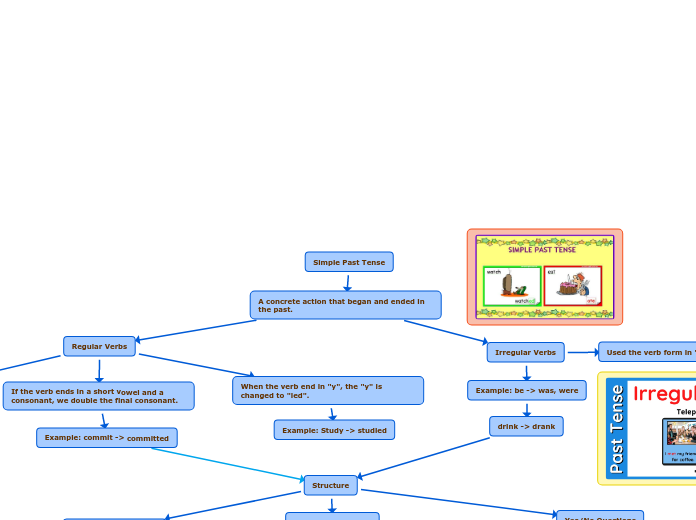
The content focuses on the differences between the simple past and the present perfect tenses, highlighting their structures and uses. The simple past is used for actions that occurred and concluded at a specific time in the past, often accompanied by time expressions such as '