jonka Leila Gatbonton 25 päivää sitten
86
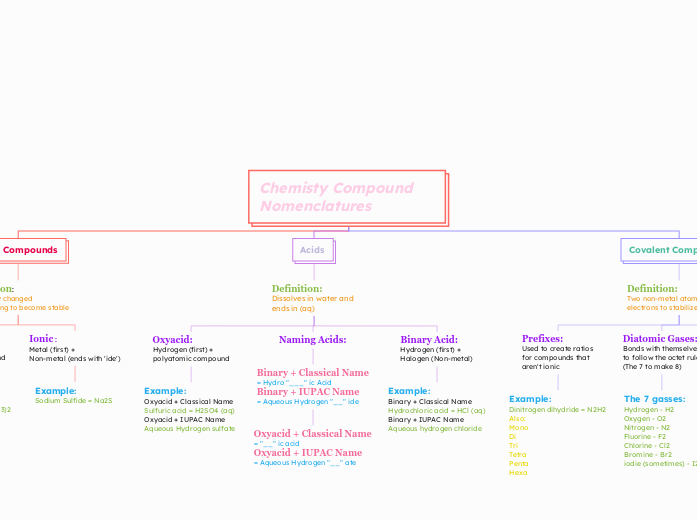
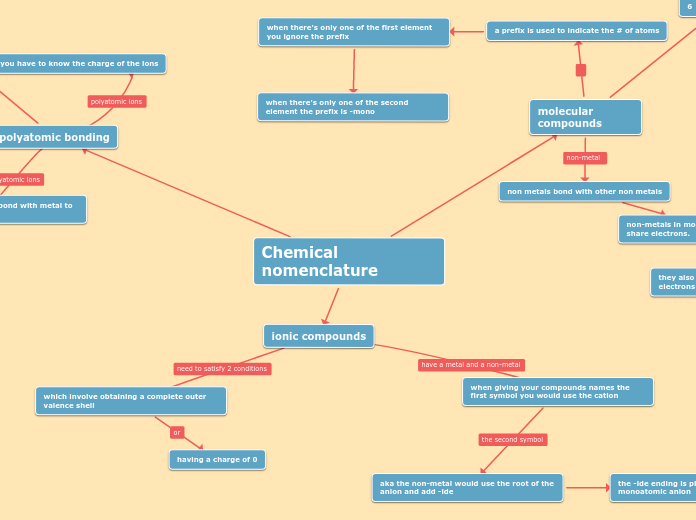
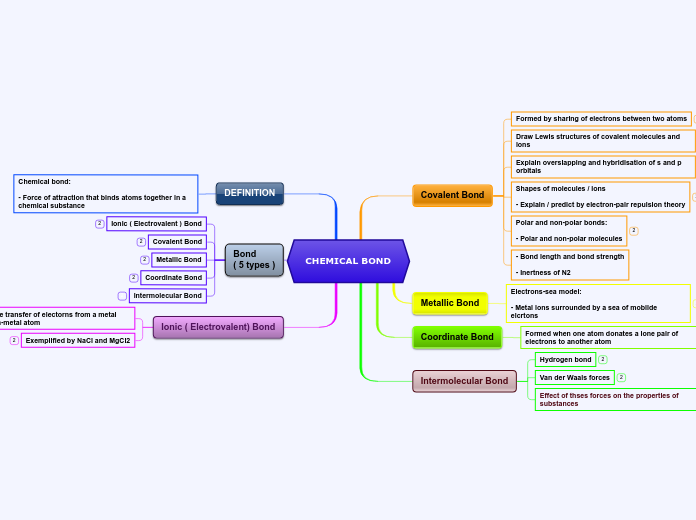
Chemisty Compound Nomenclatures
Learning the nomenclature of chemical compounds involves understanding how acids, ionic compounds, and covalent compounds are named and formulated. Acids, which dissolve in water, can be named using classical names or the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (