jonka Toheed cheema 2 vuotta sitten
101
Creation of Canada
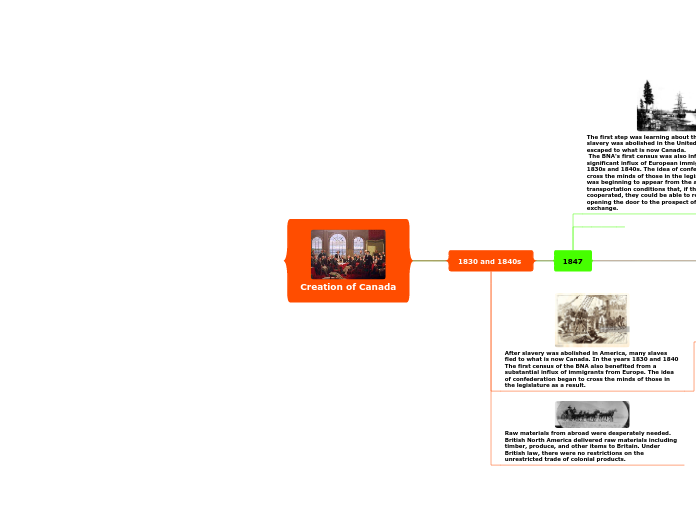
In the mid-19th century, the idea of confederation gradually took hold in British North America, driven by a combination of social, political, and economic factors. John A. Macdonald, known for his political acumen, played a crucial role in balancing the interests of different groups, including George-Étienne Cartier, who sought to protect the culture and language of the Canadiens.