Crecimiento y Control Microbiano
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
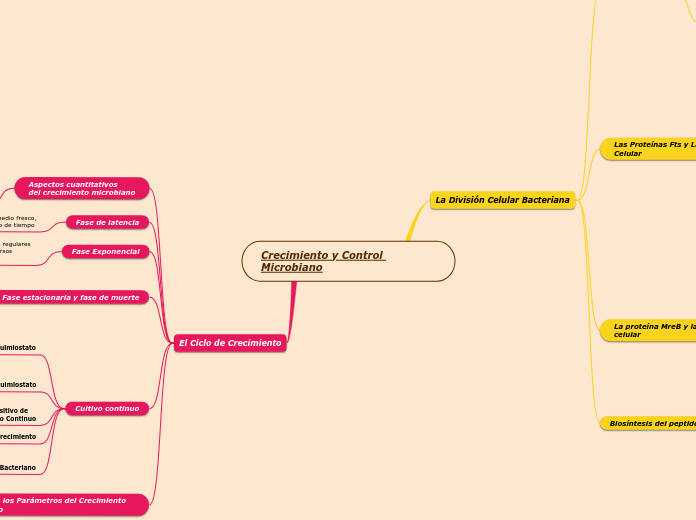
El Ciclo de Crecimiento
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Cálculo de los Parámetros del Crecimiento Microbiano
Attributive clauses serve as an attribute to a noun (pronoun) in the main clause. This noun or pronoun is called the antecedent of the clause.
Método estimación tiempo de generación
Cultivo continuo
An adverbial clause is a group of two or more words that function as an adverb in a sentence.
Fases de Crecimiento Bacteriano
Curva de Crecimiento
Describe un ciclo de crecimiento
Dispositivo de
Cultivo Continuo
Posible sortear estos cambios
Usos experimentales del quimiostato
La población de células se puede mantener en la fase de crecimiento exponencial durante largos períodos, días o incluso semanas
El quimiostato
Es un dispositivo en el que se puede controlar de manera independiente la velocidad de crecimiento (la rapidez con que se dividen las células) y la densidad celular (cuántas células se obtienen por mililitro)
Fase estacionaria y fase de muerte
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
La Densidad Óptica (Turbidez)
Medida cuantitativa dispersión de luz
En un cultivo discontinuo, el crecimiento exponencial no se puede mantener indefinidamente.
Fase Exponencial
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
La población de células se duplica en intervalos regulares durante un tiempo corto o largo según los recursos disponibles y otros factores.
Fase de latencia
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
Es un cultivo microbiano se inocula en un medio fresco,
el crecimiento empieza solo tras un período de tiempo
Aspectos cuantitativos
del crecimiento microbiano
An adverbial is an individual word (that is, an adverb), a phrase, or a clause that can modify a verb, an adjective, or a complete sentence.
Durante la división celular, una célula se convierte en dos. En el tiempo que tarda en ocurrir esto (el tiempo de generación), tanto el número de células como la masa se duplican
La División Celular Bacteriana
Biosíntesis del peptidoglicano
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
Transpeptidación
The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed.
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.
Es el paso final de la síntesis de la pared celular
Biosíntesis de peptidoglicano
The direct object is the receiver of the action mentioned in the sentence.
Se puede pensar en el peptidoglicano como una tela resistente a la tensión, muy parecida a una lámina fina de goma.
La proteína MreB y la morfología
celular
The attribute is defined as a quality or characteristic of a person, place or thing.
Evolución de la división celular y de la forma
de las células
MreB está relacionado estructuralmente con la proteína eucariótica actina, y FtsZ con la tubulina, también eucariótica.
Crescentina
Caulobacter crescentus es una especie de Proteobacteria
La forma de las células y MreB
La inactivación del gen que codifica MreB en los bacilos hace que las células tengan forma de coco (redondas).
El principal factor determinante de la forma de las bacterias es una proteína llamada MreB, que forma un citoesqueleto simple en las bacterias y en unas pocas especies de Archaea.
Las Proteínas Fts y La División
Celular
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
Replicación del genoma en las células
de crecimiento rápido
Durante la replicación bidireccional, la síntesis se produce en cada cadena molde de manera avanzada y retrasada, y esto permite que el DNA se replique lo más rápidamente posible
Replicación del DNA, proteínas Min y división
celular
La proteína MinD forma una estructura en espiral en la superficie interna de la membrana citoplasmática y ayuda a MinC a situarse en la membrana citoplasmática.
El Divisoma
FtsI
Proteína emparentada con la actina
FtsA
Es una de las varias proteínas de unión a la penicilina presentes en la célula.
ZipA
Es un anclaje que conecta el anillo FtsZ
Las proteínas Fts interaccionan en la célula para formar un aparato de división llamado divisoma.
Serie de proteínas presentes en todas las bacterias
Bacteria Grampositiva
Bacillus subtilis
Bacteria Gramnegativa
Escherichia coli
FtsZ
Proteína importante en la división celular
Fisión Binaria
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.
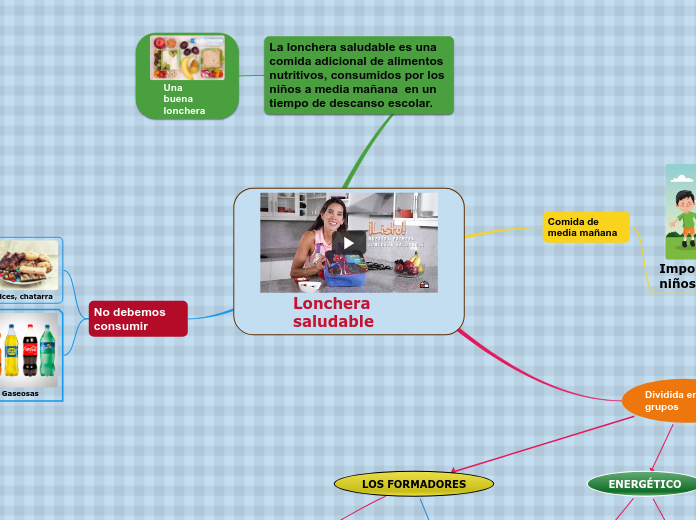
Crecimiento
Como el aumento en
el número de células.
Tiempo de Generación
Componentes celulares
aumentan proporcionalmente
(«binaria» alude a la formación de dos células a partir
de una).