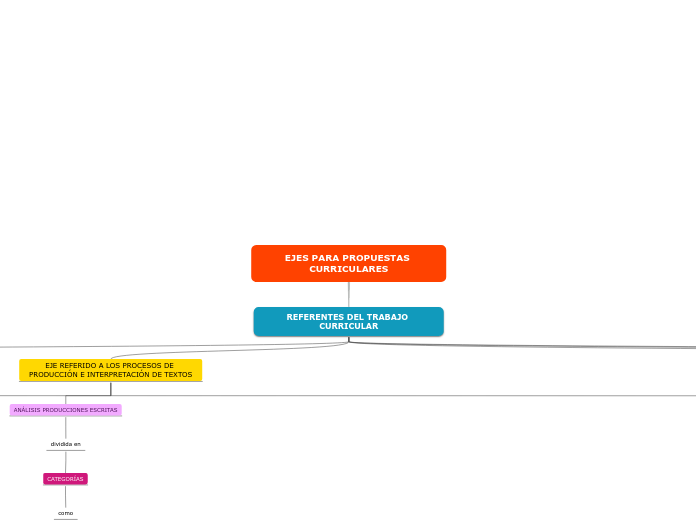
EJES PARA PROPUESTAS CURRICULARES
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
REFERENTES DEL TRABAJO CURRICULAR
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
INTERACCIÓN Y PROCESOS CULTURALES IMPLICADOS EN LA ÉTICA DE LA COMUNICACIÓN
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
DIVERSIDAD ÉTNICA Y CULTURAL
existe la
FALTA DE FORMACIÓN
EDUCADORES
para la
LECTO-ESCRITURA MATERNA
produciendo así
ABANDONO
por su
LENGUA INICIAL
LA ETNOGRAFIA
HABLA
CONSTITUYE
en una
METODOLOGÍA ESPECIALIZADA
APRENDIZAJE DE LENGUAS
ESTUDIO
resulta central el
TRABAJO
referido a
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
PROCESOS ASOCIADOS
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
PRINCIPIOS BÁSICOS
EL LENGUAJE
RESPETO POR LA DIVERSIDAD CULTURAL
DESARROLLO DEL PENSAMIENTO
ESTRATEGIAS PARA MEJORAR LA COMPRENSIÓN LECTORA
ESTRATEGIAS PARA EL APRENDIZAJE DE INFORMACIÓN
compuesta por
FORMACIÓN
EVALUAR-REGULAR
ORGANIZACIONES
relacionadas con la
CONSTRUCCIÓN-IDENTIFICACIÓN
ENSEÑANZA
ASPECTOS GENERALES
ESTRÁTEGIAS
PLANES
PROPÓSITOS DE LECTURA
COMPONENTES METACOGNITIVOS
SEGUNDO
FUNCIÓN EJECUTIVA
los cuales
COORDINAN ACTIVIDADES
e incluyen
LABORES
REGULACIÓN
PLANIFICACIÓN
EVALUACIÓN
PRIMERO
relacionado con
REFLEXIONAR
PROCESO DE COMPRENSIÓN
ESTRATEGIAS PARA FAVORECER LA COMPRENSIÓN TEXTUAL
PARAFRASEO
buscar que los
ESTUDIANTES
escriban con sus
PROPIAS PALABRAS
lo que
ENTENDIERON
RECUENTO
facilita la
DESPUÉS DE LA LECTURA
se busca
HABILITAR
a los
NIÑOS
RECONSTRUIR
REDES CONCEPTUALES
HABITAN EN ÉL
ACTIVIDADES ANTES Y DESPUÉS DE LECTURA
se puede
DIALOGAR
sobre el
POSIBLE CONTENIDO
DESTREZAS
deben
PROMOVERSE
PROCESO LECTOR
HERRAMIENTAS LINGÜÍSTICAS
son
ADQUIRIDAS
mediante la
INTERACCIÓN SOCIAL
luego se
INTERNALIZAN
para ser
USADAS CONTEXTUALMENTE
se refiere a
LAS ESTRUCTURAS
PENSAMIENTO
ADQUIEREN
mediante el
ENFRENTAMIENTO
REALIDAD EXTERNA
PROCESOS CULTURALES Y ESTÉTICOS ASOCIADOS AL LENGUAJE
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
POSIBILIDAD DE TRABAJO CON LA LITERATURA
EL ESTUDIO RIGOROSO
LITERATURA ESCOLAR
depende de la
COMPETENCIA LITERARIA-CRÍTICA
PROFESOR
EL PAPEL DE LA LITERATURA
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
PARADIGMAS
PROFUNDIZAR
ESTUDIO LITERARIO
desde
LA SEMIÓTICA
LA HISTORIOGRAFIA
LA ESTÉTICA
entendida como
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
relacionados a
ÁMBITOS TESTIMONIALES
en las que se
IDENTIFICAN
OBRAS
AUTORES
MOMENTOS HISTÓRICOS
RASGOS ORALES
TENDENCIAS
LUGAR
CONVERGENCIA
CIENCIAS
MANIFESTACIONES HUMANAS
de lo
SUSCITACIÓN
ESTÉTICO
EJE REFERIDO A LOS PROCESOS DE PRODUCCIÓN E INTERPRETACIÓN DE TEXTOS
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
CONCEPTUALIZACIÓN DEL PROCESO LECTOR
LEER
PROCESO
CONSTRUCCIÓN DE SIGNIFICADOS
a partir de la
INTERACCIÓN
EL CONTEXTO
alude a las
CONDICIONES
RODEAN
ACTO LECTOR
divididos en
EL PSICOLÓGICO
referido al
ESTADO DE ÁNIMO
LECTOR
al momento de
EL EXTRATEXTUAL
compuesto por
FACTORES CLIMÁTICOS
o también
ESPACIOS FÍSICOS
donde se realiza la
EL TEXTUAL
representado por
IDEAS
situadas
ANTES Y DESPUÉS
ENUNCIADO
EL TEXTO
determinado por la
INTENCIÓN COMUNICATIVA
y a su vez por la
entre las
ORACIONES
hasta
CONCLUIR
HILO ARGUMENATAL
TEMA
formado por
PROPOSICIONES
RELACIONAN ENTRE SÍ
por medio de
LAZOS FORMALES
que ayudan a
DETERMINAR
SIGNIFICADO TEXTUAL
EL LECTOR
emplea
ESTRATEGIAS
INFERENCIA
VIRTUD
DEDUCIR-CONCLUIR
COMPONENTES IMPLICITOS
ESCRITO
PREDICCIÓN
FACULTAD
para
ANTICIPAR
CONTENIDOS
MUESTREO
CAPACIDAD
que
POSEE
el lector para
SELECCIONAR
las
PALABRAS-IDEAS SIGNIFICATIVAS
encontradas en el
para construir los
SIGNIFICADOS
ANÁLISIS PRODUCCIONES ESCRITAS
dividida en
CATEGORÍAS
esta configurada por
SUPERESTRUCTURA
referida a e
SELECCIONAMIENTO
TIPO DE TEXTO
y el
PRINCIPIO LÓGICO
ORGANIZACIÓN
LA INTENCIÓN
POSIBILIDAD
RESPONDER
a un
REQUERIMIENTO
referida a los
ELEMENTOS PRAGMÁTICOS
relacionados con la
PRODUCCIÓN ESCRITA
COHERENCIA Y COHESIÓN LINEAL
se
GARANTIZA
con el
EMPLEO
RECURSOS COHESIVOS
como los
SIGNOS DE PUNTUACIÓN
SEÑALIZADORES
cumpliendo así una
LÓGICA ESTRUCTURAL
CONECTORES
se define al rededor de la
COHERENCIA LINEAL
referida a
LA LLACIÓN
PROPOSICIONES ENTRE SÍ
COHERENCIA GLOBAL
constituye un
SENTIDO
de dar
CUENTA
GLOBALIDAD
SEGUIMIENTO
de un
NÚCLEO TEMÁTICO
a lo largo de la
PRODUCCIÓN
vista como
PROPIEDAD SEMANTICA
COHERENCIA Y COHESIÓN LOCAL
evidencia las
CONCORDANCIAS PERTINENTES
SEGMENTACIÓN
GÉNERO-NÚMERO
SUJETO-VERBO
entendida como la
REALIZACIÓN
ENUNCIADOS
constituye el
NIVEL MACROESTRUCTURAL
referida al
NIVEL INTERNO
PROPOSICIÓN
dividido en
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
PROCESOS EXTRATEXTUALES
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of viewSecond person point of viewThird person point of viewOmniscient point of view
se basa en la
RECONSTRUCCIÓN
CONTEXTO COMUNICATIVO
en donde
APARARECEN
los
TEXTOS
PROCESOS INTERTEXTUALES
posibilita el
RECONOCIMIENTO
de las
RELACIONES
del
ÉPOCAS
VOCES EN EL TEXTO
DEMÁS TEXTOS
TEXTO
PROCESOS INTRATEXTUALES
ligado a
ESTRUCTURAS
PRESENCIA
MACROESTRUCTURAS
MICROESTRUCTURAS
SINTÁCTICAS
UN EJE REFERIDO A LOS PROCESOS DE CONSTRUCCIÓN DE SISTEMAS DE SIGNIFICACIÓN
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
NIVEL METACOGNITIVO
ETAPAS DEL DESARROLLO DE LA ESCRITURA
NIVEL 3
aparece la
RELACIÓN
SONIDO
GRAFÍA
dando paso a la
HIPÓTESIS SILÁBICO ALFABÉTICA
NIVEL 2
aparece un
CONTROL
sobre la
CANTIDAD
CUALIDAD
buscando
DIFERENCIAS
ESCRITURAS
que justifiquen
INTERPRETACIONES DIFERENTES
NIVEL 1
existe una
DISTINCIÓN
entre
LENGUAJE ICÓNICO
y
GRAFÍAS
como forma de
REPRESENTACIÓN
es necesario
el nivel cuando
EXISTA
un buen
para el
USO LINGÜÍSTICO
referido a la
TOMA DE DISTANCIA
y la
REGULACIÓN CONSCIENTE
SISTEMAS DE SIGNIFICACIÓN
con
FINALIDADES
COMUNICATIVAS-SIGNIFICATIVAS
NIVEL DE EXPLICACIÓN DEL FUNCIONAMIENTO
este
NIVEL
se debe
TRABAJAR
con mayor
INTENSIDAD
luego de un buen
COMPETENCIAS LINGÜÍSTICAS
EXPLICACIÓN
de los
FENÓMENOS LINGÜÍSTICOS
debe darse en
ACTOS COMUNICATIVOS SIGNIFICATIVOS
propone
OBJETOS DE ESTUDIO
EL CINE
LA IMAGÉN
LA LENGUA
PRAGMÁTICA
SINTAXIS
ORTOGRAFIA
permiten
EXPLICAR-COMPRENDER
como
FUNCIONA
LENGUAJE
LINGÜÍSTICA DEL TEXTO
TEORÍA GRAMATICAL
está
RELACIONADO
con la
REFLEXIÓN SISTEMÁTICA
sobre los
ESTUDIOS
NIVEL DE USO
supone el
DESARROLLO
COMPETENCIAS
ENCICLOPÉDICAS
SINTÁTICAS
SEMÁNTICAS
PARAGMATICÁS
se encuentra
ASOCIADO
con las
PRÁCTICAS
de
LENGUAJE DE LA IMAGÉN
ORALIDAD
y las
FUNCIONES
que se
ASIGNAN
a esta
PRÁCTICA
ESCRITURA
LECTURA
NIVEL DE CONSTRUCCIÓN
CONOCIMIENTO
HISTORIA
de este
SISTEMA
ELEMENTO CENTRAL
permite
IDENTIFICAR
en que
MOMENTO
se pone
ÉNFASIS
la
CONSTRUCCIÓN-APROPIACIÓN
de estos
SISTEMAS
el manejo del
CÓDIGO ALFABÉTICO CONVENCIONAL
es un
PUNTO DE LLEGADA
en el
DESARROLLO NATURAL
NIÑO
está referido al
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
REFERENTES DEL TRABAJO CURRICULAR.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
TRABAJO PEDAGÓGICO
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
permitiendo la
CONSTRUCCIÓN
de la
SIGNIFICACIÓN
en
COLOMBIA
el
SISTEMA PRINCIPAL
es la
LENGUA CASTELLANA
y el paso a la
COMUNICACIÓN