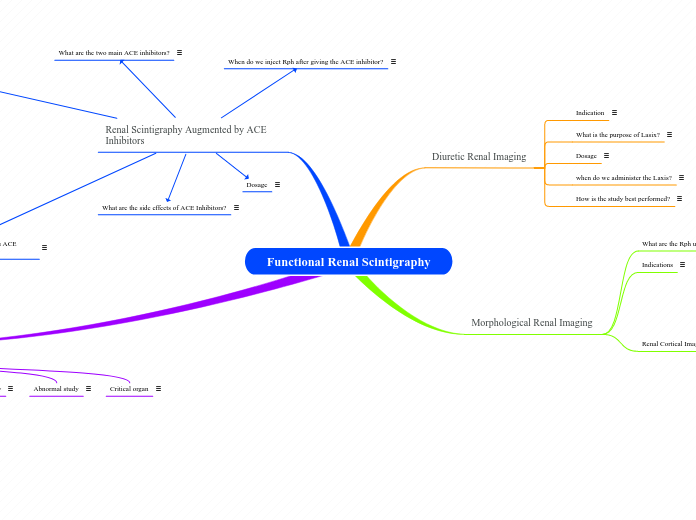
Functional Renal Scintigraphy
Vesicoureteral Reflux Study
Critical organ
Bladder (18mrads/mCi)
Abnormal study
Activity seen in the upper urinary tract during filling, full capacity and while voiding
Normal study
No visible reflux and all of solutionis voided from bladder
patient position
sitting/supine with kidneys and bladder in FOV
Method of localization of Rph
Compartmental with flow of urine
How radionuclide cystography can be performed?
By catherizing the patient and directly instilling the radionuclide into the bladder or by injecting the patient with the tracer as it is excreted by the kidneys.
Direct catheteriziation has a higher sensitivity and specificity than the indirect method and is the preferred method for radionuclide cystography.
Tc99m pertechnetate, DTPA or Sulfur Colloid can be used
Dose range: .5-1mCi
Used for the evaluation of children with suspected vesicouretal reflux; It is the initial investigation of choice in selected children with urinary tract infections.
Renal Scintigraphy Augmented by ACE Inhibitors
What does a positive study indicates for a patient hypertension?
It indicates that the hypertension is renin dependant, most likely produced by RAS, and it can be improved by renovascularization
When should medications be stop , if patient takes ACE inhibitors?
48hrs for captopril and a week for enalaprilat before study
When do we inject Rph after giving the ACE inhibitor?
Radiopharmaceutical is administered 60 min after ACE inhibitor
Captopril: 25-50mg orally dissolve in 150-200ml water to enhance absorption
Enalaprilat: 40ug/kg in 10ml of normal saline; slow intravenous push over 3-5min to avoid any reaction.
What are the side effects of ACE Inhibitors?
Captopril side effects include hypotension, dizziness, tachycardia, chest pain, rash, and loss of taste.
Adverse side effects of enalaprilat include orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, chest pain, headache, dry cough, electrolyte disturbances, fatigue, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea
What are the two main ACE inhibitors?
The two most commonly used are Captopril (Capoten) and Enalaprilat (Vasotec IV)
Morphological Renal Imaging
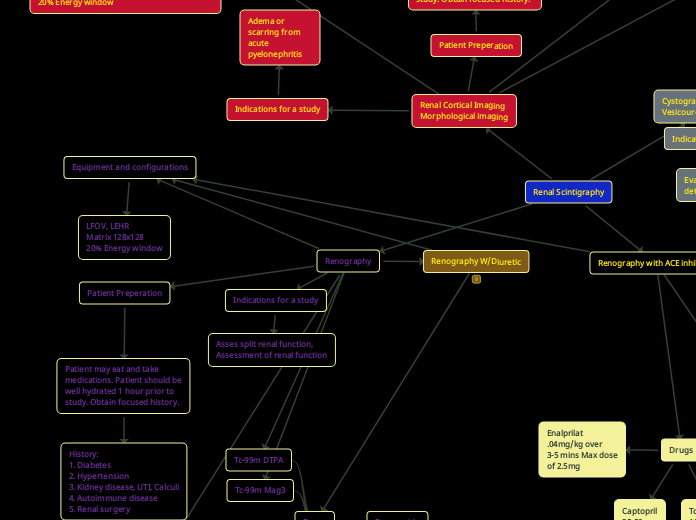
Renal Cortical Imaging
Evaluate edema or scarring from acute pyelonephrotitis
Confirmation of suspected hypertrophied column or berlin
Interpretation
normal: smooth renal contour; symmetrical distribution of rph in each kidney and equal concentration in renal cortex
Abnormal: Acute pyelonephritis appears as single or multiple defects resulting in decrease uptake. In differentiating the column of Berlin from a actual mass, the DMSA scan will demonstrate uptake in the column of Berlin but not in a mass caused by a tumor.
Instrumentation
20% window with an energy of 140KeV
Static images are taken 2hrs after rph administration
500000 total cts for each images for a total of 5 images
Views: POST/RAO/LAO/RPO/LPO of the kidneys
Used low field of view with parallel hole collimators for differential calculations
Used pin hole collimator for cortical images
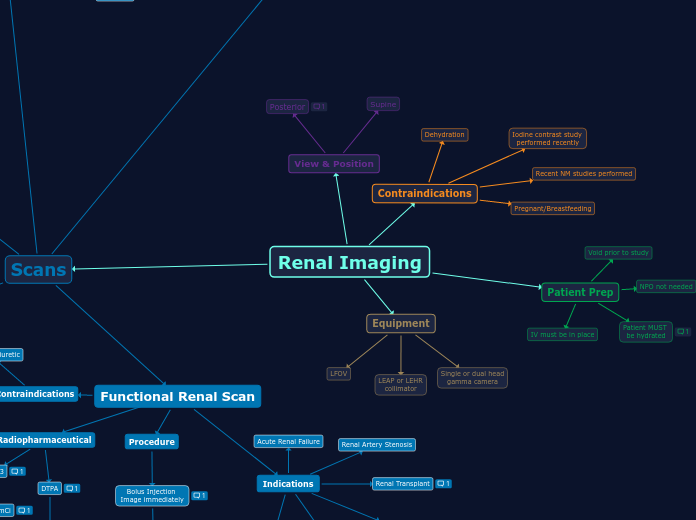
Contraindications
Pregnancy
Tc99m GH
secreted by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion
permits visualization of renal blood flow and imaging of renal cortex
renal clearance is about 50% at 3hrs
Adult: 10-15mCi
Children: 200uCi
Dose
DMSA
Adults: 5mCi-10mCi
Children: 50uCi
Tc99m DMSA
Taken up by renal cortex
90% bound to plasma proteins which prevents significant glomerular filtration
The DMSA molecules splits upon reaching the kidneys
16% of DMSA will be in the urine 3hrs after injection
Indications
Used to document global and regional changes in renal function;In patients with acute pyelonepritis, areas of decreased frunction may improved with treatment. In children with vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) and a history of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Detect the presence or absence of small renal infarction. Sometimes it is used to differentiate a prominent column of Berlin seen in ultrasound; The detection of hypertrophied columns of Berlin is important because it alleviate biopsy and radical surgeries.
What are the Rph used?
Tc99m-DMSA and glucoheptonate
Diuretic Renal Imaging
How is the study best performed?
Using 10mCi of Tc-MAG3 is the best option
Tc99m-DTPA can also be used
when do we administer the Laxis?
If the tracer in the renal pelvis or calyces at the conclusion of renal function imaging, the administration of a diuretic to rule out urinary tract obstruction is given
Dosage
20-40mg in adaults
.5-1mg/kg in pediatric patients
It is injected over 1-2min.
1-2min or 2-5min effects are visible
What is the purpose of Lasix?
Furosemide is a loop diuretic that acts on the kidneys to increase water loss from the body; an anthranilic acid derivative. By increasing urine flow, a functional obstruction can be overcome by increasing pressure in the renal pelvis and thus allowing urine flow from the collecting system into the ureter to the bladder. This allows the documentation of the diuretic urodynamic and differentiation of a fixed anatomic from functional abnormality.
Indication
Differentiate a dilated renal collecting system from an obstructed renal collecting system