RNA Splicing
Removing Introns
Ribozyme: attaches to pre-mRNA sequences and remove introns
Spliceosome: a complex region of small RNAs and proteins
Replication
DNA to DNA
DNA
ORI sequences
short stretches of DNA that have a specific sequence of nucleotides.
Prokaryotic Chromosome
*replication is BIDIRECTIONAL*
Proteins that initiate DNA replication recognize this sequence and attach to the DNA, separating the two strands and opening up a replication “bubble”
circular and has a SINGLE origin.
Eukaryotic Chromosome
linear stretch of DNA and have hundreds or even thousands of origins of replication
ENZYMES/PROTEINS IN DNA REP
DNA ligase
joins Okazaki fragments of lagging strand
DNA pol III
Using parental DNA as a template, synthesizes new DNA strand by adding nucleotides to the 3’ end of the primer OR a pre-existing DNA strand
DNA pol I
Removes RNA nucleotides of the primer from the 5’ end and replaces them with DNA nucleotides added to the 3’ end of adjacent fragment
Primase
synthesizes the RNA primer at the 5’ end of leading strand and at 5’ end of Okazaki fragment of lagging strand.
Topoisomerase
relieves the tight strain from the untwisting of the DNA strand
Single Stranded Binding Protein
bind to each UNPAIRED DNA strand and keep them from forming back into the double helix
Helicases
BREAK HYDROGEN BONDS. It untwists the double helix at the replication forks, separating the two parental strands and making them available as template strands.
Structure: double helix, phosphate-sugar backbone outside the DNA molecule, each strand is anti-parallel to one another.
Nitrogenous Bases:adenine (A) with thymine (T), and guanine(G) with cytosine (C).
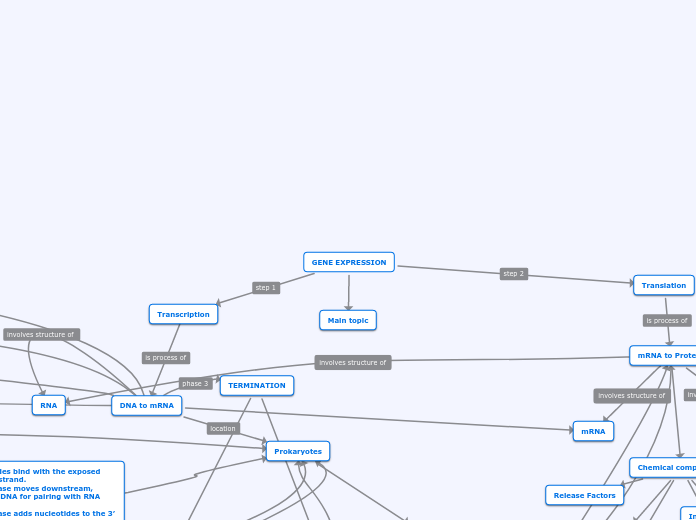
GENE EXPRESSION
Main topic
Transcription
DNA to mRNA
mRNA
TERMINATION
•RNA polymerase II transcribes a sequence of DNA called the polyadenylation signal sequence. This sequence specifies a polyadenylation signal (AAUAAA) in the pre-mRNA which causes the RNA polymerase II to cut the pre-mRNA transcript free
Eukaryote Modifications
occurs in the nucleus
Second Modification
First Modification
50-250 adenine nucleotides are added to form a poly-A-tail.
after the polyadenylation signal is transcribed (after transcription ends)
•At the end of the DNA sequence, RNA polymerase reads through and transcribes the terminator sequence
•Transcription is halted
•RNA polymerase disassociates from the DNA sequence, releasing mRNA
INITIATION
Transcription factors, a collection of proteins, mediate the binding of RNA polymerase II and the initiation of transcription. *transcription factors MUST attach to the promoter first before RNA polymerase II can bind to it. *
RNA polymerase II binds to the promoter. In Eukaryotes, the promotor is typically a TATA box upstream from the transcription start point.
DNA strands unwind
mRNA is transcribed at the start point on the template strand
RNA polymerase II initiates pre-mRNA synthesis at the transcription start point on the template strand
ELONGATION
•RNA nucleotides bind with the exposed DNA template strand.
•RNA polymerase moves downstream, unwinding the DNA for pairing with RNA nucleotides
•RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing pre-mRNA molecule. (that means the template strand runs from 3’-5’)
•DNA strands are also formed back into a double helix
• Pre-mRNA nucleotides bind with the exposed DNA template strand.
• The RNA polymerase II moves downstream, unwinding the DNA for pairing with RNA nucleotides
• RNA polymerase II adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing pre-mRNA molecule. (that means the template strand runs from 3’-5’)
• DNA strands are also formed back into a double helix
RNA polymerase I: yields pre-MRA and MRNA during transcription
Eukaryotes
occurs in the nucleus, and the final mRNA is transported to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Prokaryotes
occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm, and the mRNA is simultaneously converted into amino acid sequences of a polypeptide by the ribosomes.
RNA
Translation
mRNA to Protein
Chemical components
Release Factors
Elongation Factors
Initiation Factors
Peptidyl transferase: Formation of peptide bonds between amino acids
Amino Acids: Brought to the ribosome by tRNA and is attached to the growing chain of polypeptides.
mRNA : contains codons which code for a specific amino acid
tRNA: transfer RNA: the amino acid is attached to the 3’ end of the tRNA
tRNAs have an ANTICODON. This anticodon matches the codon of the mRNA nucleotide
Ribosomes
-small subunit and large subunit: where the amino acids are assembled into a polypeptide
Amino Acyl tRNA synthetase
this is the enzyme that helps ADD the amino acid to the 3’ end of the tRNA.
Proteins