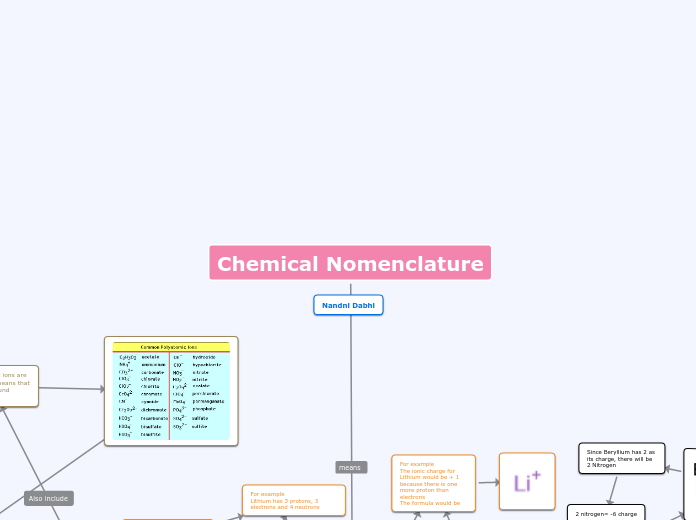
Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
- A attractive force between a positive component and a negative component of molecules
Ester Linkages
- Triglyceride and Phospholipids are formed by condensation reactions and broken apart by Hydrolysis reactions
- the hydroxyl group with glycerol reacts with carboxylic acid of the fatty acids to form a ester linkages
Introduction To Biochemistry
Biochemical Reactions and Functional Groups
Redox reaction
Add Oxygen is oxidation
Lose Hydrogen is oxidation
Gains hydrogen is reduced
Remove oxygen is reduced
RH2 + B -> R + BH2
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation:
R +ATP -> R-PO4 + ADP
Neutralization
A Neutralization reaction occurs when a acid and base react to create a water and a salt
ex.
HCL + NaOH = NaCl + H2O
Ester/Amide/Phosphodiester
- Ester - a organic compound where the hydrogen in a carboxyl group is replaced with a hydrocarbon group
- Amide - an organic compound that contains a functional acyl group ( R-C=O ) linked to a nitrogen atom
- Phosphodiester - the linkage between the 3' carbon of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon of another
Isomerzation

AB<->BA
Anabolic
Condensation Reaction
( I tried to put and image here but it didn't work )
A + B --> AB + H2O
Example of an Anabolic reaction
Catabolic
Hydrolysis Reactions

AB + H20 --> A + B
Example of A Catabolic Reaction
Glycosidic
- In a saccharide , both the Ribose and Deoxyribose are bonded by a single oxygen , which is called the Glycosidic reaction
Enzymes
- Acts as a Catalyst during chemical reactions
Reactants
Product
Hydroxyl Group
R-----O-----H
- Polar Hydrophilic
- Characterized by presences of H and O
Sulfhydryl Groups
R-----S-----H
- Polar Hydrophilic
- Characterized by presence of S
Carbonyl Group
O
ll
ll
R-----C-----R
- Polar Hydrophilic
- Characterized by central C and O
- Bound to two side groups
- Double bond to oxygen increases the polarity
Ketones

Polar Hydrophilic
Characterized by Central C and O
Bound to 2 side group
Double bond to oxygen increases polarity
Aldehyde

Polar Hydrophilic
Characterized by Central C and O
Bound to 1 side groups
Double bond to oxygen increase the polarity
Phosphate group

Acidic Polar Hydrophilic
Characterized by presence of P
Intramolecular Forces
- Forces within molecules that hold atoms together
Non-polar/Polar
- Two non-metals share electrons equally
- Two non-metals share electrons unequally
Covalent Bonding
- The sharing of electrons between Atoms
Ionic Bonding
- A metal loses a electron, becomes a +ve cation, to a nonmetal, that gains a electrons becomes a -ve anion
- -ve and +ve are electrostatically attracted
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Hormones
- Chemical messengers that coordinate different functions in your body
Neurotransmitter
- Chemical Messengers
- their job is to carry chemical signals from one neuron to another
Fair Test
- A test that controls all but one variable when trying to answer a question
Lipids
Independent/Dependent, and Controlled Variables
- Independent - the variable that is altered during a scientific expiriment
- Dependent - the variable being tested or measured
- Controlled - a variable that stays the same
Nucleaic Acid
Potential energy
- energy that has the potential to become another form of energy
Double Helix
- a DNA strand is made of of two linked strand that wrap around each other , resembling a twisting ladder ( helix shape )
Autotrophs/Heterotrophs
- Autotrophs are able to make their own food using raw materials / energy ( producers )
- Heterotrophs must consume other organisms in order to get food ( consumers )
ATP
- Adenosine Triphosphate, a Nucleotide
- Made up of a Phosphate group , a sugar ( ribose ) , and a Nitrogenous Base ( adenine )
NAD+/NAPD+/FAD+
- NAD+ consist of 2 phosphate group, 2 sugar ( ribose ) , and 2 nitrogenous base ( 1 adenine , 1 cytosine )
- NADP+ consist of 3 phosphate group , 2 sugar ( ribose ) , and 2 nitrogenous base ( 1 adenine , 1 cytosine )
- FAD+ consist of 2 phosphate group , 2 sugar ( 2 ribose ) , 2 nitrogenous base ( 1 adenine , 1 Guanine )
Ribose/Deoxyribose
- Both are Pyrimidines
- both have a 5' and 3' carbon
- The difference is ribose has a hydroxyl functional group on the 2' carbon, but deoxyribose does not
Nucleotide
- the building blocks/monomers of Nucleaic Acids
Phosphodiester Bond
- a phosphate with 4 oxygens , on of them is double-bond
- Makes up ATP
Nitrogenous Base
- Adenine
- Purine
- Makes up ATP
Transmembrane Protein
- a integral protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane
Glycolipid/protein
- a lipid/protein with a carbohydrate added to it
Triglyceride
- they function as long term energy storage molecules
- the carbon chains are a source of carbon to enter the Krebs cycle producing NADH for the electron transport chain
Phospholipids
- Make up majority of the Cell Membrane
- They consist of a hydrophobic head , made up of a polar group, a phosphate group , glycerol , and a hydrophobic fatty acid
Mosaic
Cell Membrane is made up of :
- Phospholipids
- Integral proteins
- Peripheral proteins
- Channel Proteins
- Alpha-Helix proteins
- globular proteins
- Glycolipids
- Glycoproteins
- Cholesterol
Steroids
- They function a signaling molecules and components of the cell membrane
- Testosterone , estradiol , and progesterone are hormones involved in the reporductive system
- only experience L.D.F, non-polar , hydrophobic , and insoluble
Amphipathic
- have both polar/non-polar regions
- mostly hydrophobic
Micelle
Bilayer
- A double layer of closely-packed lipids
Fatty acids
- Long Hydrocarbon Chains that end in a carboxyl groups
- the carbon chains can be un/saturated or have single/double bonds
Glycerol
- a 3 carbon molecule with 3 hydroxyl groups
Waxes
- Are Waterproofing Layers
- Only expeirence L.D.F
- Long , Straight Chains
Hydrophobic/philic
- phobic - fear of water
- philic - attract to water
Primary,Secondary,Tertiary,Quaternary Structures

Primary (a) - the sequence of amino acids
Secondary ( b ) - The localized structure as to whether or not the amino acid sequence forms a alpha-a-helix or beta-b-pleated based on hydrogen bonding
Tertiary ( c ) - a 3D structure based on other intermolecular forces including ionic bonds , hydrogen bonds , disulfide bridges , and hydrophobic interactions
Quaternary ( d ) - a 3D structure where more than one polypeptide chain is involved
Peptides/Polypeptides
- Peptides - a short chain of amino acids
- Polypeptides - a complex structure of amino acids made by peptides
Amino acids and Essential Amino Acids
- Amino Acids are the monomer of protein ,made up of a amine and carboxyl group , with a central carbon with a h and r group
- Essential Amino Acids are acids we need to obtain our diet because we don't have metabolic processes to process them
R-groups
- the unique portion of amino acids that defines its properties
Monosaccharides
- The Monomers of Carbohydrates
- Contains Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Groups
Isomers
- Molecules with the same number and type of atoms , but arranged differently
Aldose and Ketose
- Aldose and Ketose are both Monosaccharides
Essential Nutirenst
- Nutrients we need in order to survive
Macronutrients
- Molecules that livings things need in a relatively large amount to live
Monomers
- Molecules that bond together in order to make more complex structures i.e polymers
Polymers
- A structure of molecules made by smaller molecules called Monomers
Polysaccharides
- Starch - a Branch Polysaccharide found in plants, made up of amylose and amylopectin
- Amylose - made up of glucose molecules chain
- Amylopectin - a branch chain of glucose with a 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic linkages
Oligosaccharides

Disaccharides
 -
-
Glycosdic Linkage
- A chemical Bond that forms between two Monoasccharides in a Condensation Reaction
Intermolecular Forces
- The force that mediates interactions between bonds
London Dispersion Forces (Van Der Waals Forces )
- A slight attraction develops between the oppositely charged regions between nearby regions
- Same as London Dispersion Forces
Dipole-Dipole Forces
- Forces between polar molecules , opposite poles match up by electrostatic attraction
Ion-Dipole Forces
- Forces between a polar molecule and a non polar molecule
Hydrogen Bonds
- A strong inter molecular force of attraction between a partially positive hydrogen and a partially negative Oxygen , Nitrogen , or Fluorine ( HNOF )