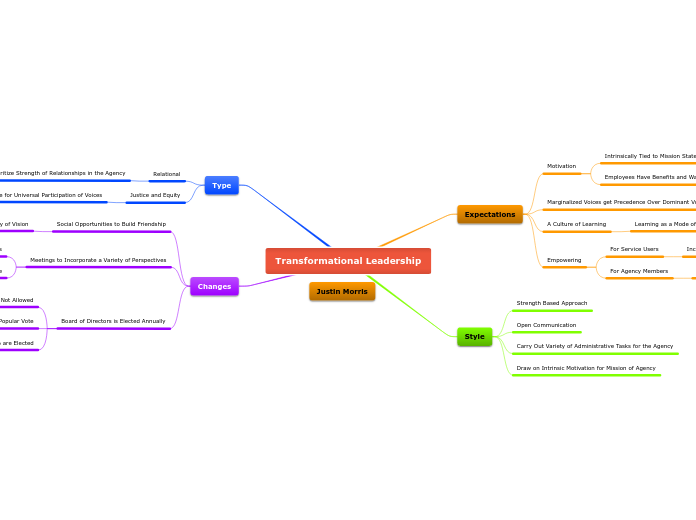
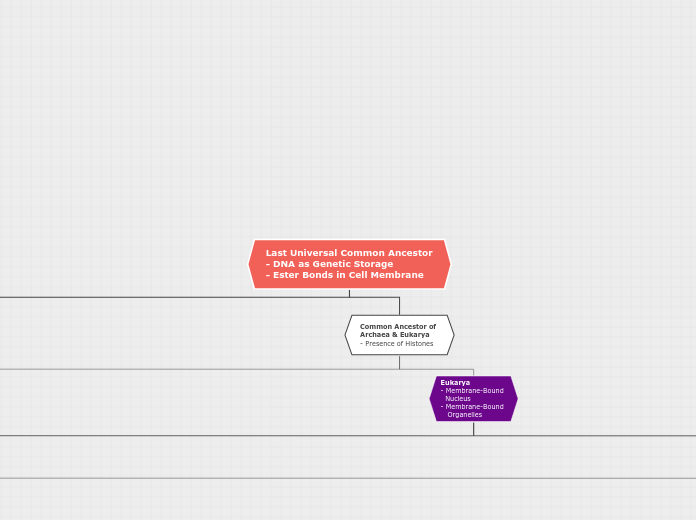
jonka Khorramshahi Kian 7 vuotta sitten
592
Kian Khorramshahi, Physical Anthropology
The study of human evolution encompasses various scientific disciplines including anthropology, genetics, and primatology. Human beings, like other primates, exhibit significant anatomical and genetic diversity.