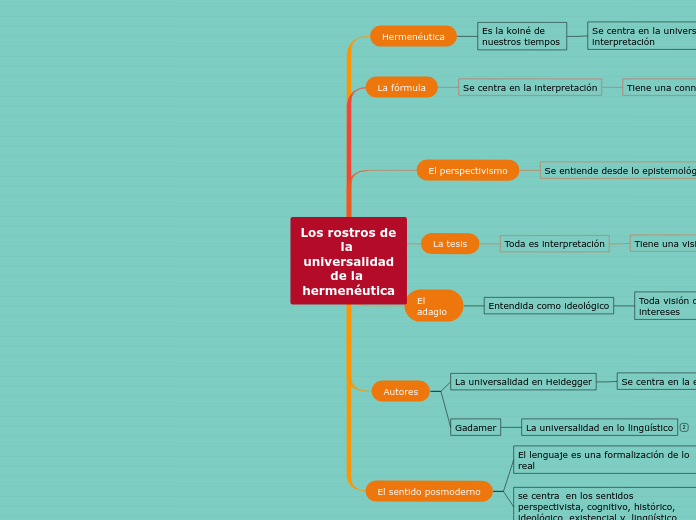
Los rostros de la universalidad
de la hermenéutica
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
El sentido posmoderno
se centra en los sentidos perspectivista, cognitivo, histórico, ideológico, existencial y lingüístico,
El objeto de la hermenéutica se comprende a partir de la idea de un sentido interior, inagotable, que buscamos interpretar a través de sus expresiones externas.
El lenguaje es una formalización de lo real
su interpretación es englobante
Autores
Gadamer
La universalidad en lo lingüístico
Es primero para Gadamer el de
las cosas mismas más que ser el de nuestro espíritu
El objeto de la comprensión es lingüístico
La universalidad en Heidegger
Se centra en la existencia
La autenticidad destruye malas interpretaciones
Interpretar es comprender las cosas
Interpreta desde la facticidad
El adagio
Entendida como ideológico
Toda visión del mundo dirigido por intereses
Se llega a una verdad si se libera de las ideologías
Solo se llegue a una realidad ideal.
Se hace referencia a Marx y a Freud
La tesis
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
Toda es interpretación
This is the moment when the main character surpasses the last obstacle and finally faces their greatest challenge.
The climax usually follows one of these patterns:
- realization
- resolution
- choice
Type in your answer.
Tiene una visión historicista
Comprender desde el contexto
Es de la hermenéutica clásica y metodológica
El perspectivismo
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
Se entiende desde lo epistemológico
There wouldn't be any tension and excitement in your story if there weren't any obstacles in your character's way.
La verdad sujetos a revoluciones científicas
Toda ciencia opera desde desde la representaciones del mundo
No ha conocimientos sin esquemas, paradigmas según Thomas Kuhn
A story is nothing more than a character overcoming a series of difficulties to reach the desired goal. Obstacles usually create suspense and conflict. In overcoming obstacles, there is growth: weak becomes strong; hatred turns into love; sadness into happiness; wrong into right; lies into truth; or evil becomes good.
See a few examples below:
- stopping a meteor
- finding a killer
- finding love
La fórmula
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
Se centra en la interpretación
The setting (time & place) of a story can change throughout the plot.
Tiene una connotación Nietzscheano
Sensory details include sight, sound, touch, smell, and taste. These details are important because they create depth in your setting.
See a few examples below:
- the smell of fresh bread
- the scent of freshly cut grass
- rain falling onto the windshield etc.
Solo es una perspectiva dictada por la voluntad
No hay verdad solo adecuación
No hay hechos solo interpretaciones
Hermenéutica
Es la koiné de nuestros tiempos
Se centra en la universalidad de la interpretación
Encaminada a la verdad