Organizing Important Terms
Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
Different Types of Attraction
Hydrophobic Interactions(learned in grade 11)
When non-polar molecules clump together to avoid contact with water molecules.
Dipole
This occurs between two polar molecules where the positive end of one attracts to the negative of another. This is caused by differences in electronegativity between atoms. This makes them attract.
Dispersion
Usually the electrons in a molecule are evenly distributed but sometimes they all go to one side which creates a mini negative force and repels electrons in any nearby molecule. And they attract.
Ionic Bonding
This happens when a molecule has electrons that aren't shared equally which means it is either positive or negative and attracts the opposite of a molecule nearby.
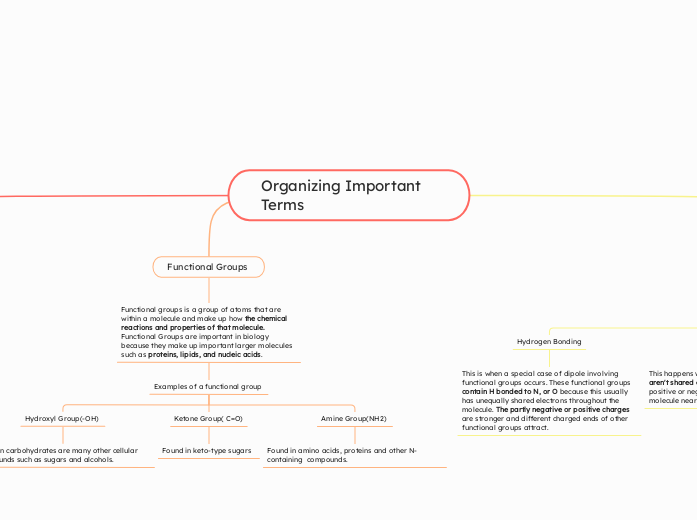
Hydrogen Bonding
This is when a special case of dipole involving functional groups occurs. These functional groups contain H bonded to N, or O because this usually has unequally shared electrons throughout the molecule. The partly negative or positive charges are stronger and different charged ends of other functional groups attract.
Functional Groups
Functional groups is a group of atoms that are within a molecule and make up how the chemical reactions and properties of that molecule. Functional Groups are important in biology because they make up important larger molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Examples of a functional group
Amine Group(NH2)
Found in amino acids, proteins and other N-containing compounds.
Ketone Group( C=O)
Found in keto-type sugars
Hydroxyl Group(-OH)
Found in carbohydrates are many other cellular compounds such as sugars and alcohols.
Polarity
Non-Polar
Non-Polar molecules have equally shared electrons and no charge distribution
Example: Lipids like oils or fats
This results in the non-polar molecules being unable to dissolve efficiently in water(hydrophobic)
Polar
Polar Molecules have areas with slight charges(ex. water)
Water has partial Positive Charges on Hydrogen and Partial Negative ends on Oxygen
This results in water being able to form hydrogen bonds and dissolve other polar molecules.