jonka Rumaysa Khan 2 vuotta sitten
164
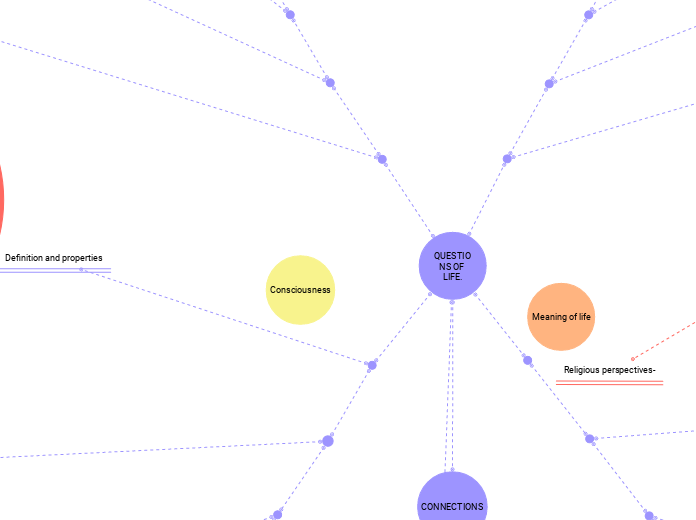
QUESTIONS OF LIFE.
The exploration of the meaning of life encompasses various fields including neuroscience, religion, and philosophy. From a neuroscientific viewpoint, consciousness is seen as the result of coordinated activity across multiple brain regions such as the prefrontal cortex, parietal cortex, and thalamus.