Theories of Leadership and Group Behavior
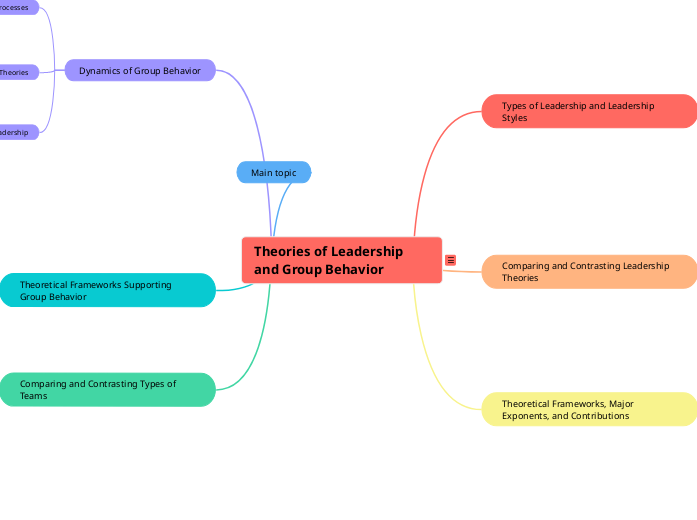
Overview: Theories of Leadership and Group Behavior
• Types of Leadership and Leadership Styles
o Autocratic/Authoritarian:
Centralized decision-making; minimal input from subordinates.
o Democratic/Participative:
Leaders involve team members in decision-making; promote collaboration.
o Laissez-Faire:
Leaders provide freedom for subordinates to manage their own tasks.
o Transactional:
Based on exchanges (reward for performance, punishment for noncompliance).
o Transformational:
Inspires change through vision, charisma, and individualized support.
o Servant/Distributed Leadership:
Emphasizes follower growth, shared responsibility, and collective decision-making.
• Comparing and Contrasting Leadership Theories
o Classical Theories:
Focus on management principles and efficiency (e.g., Weber's bureaucracy).
o Behavioral Approaches:
Analyze specific behaviors (e.g., Ohio State's "initiating structure" vs. "consideration").
o Contingency/Situational Theories:
Effectiveness depends on matching leadership style to situational factors (e.g., Fiedler's Contingency Model).
o Modern Approaches:
Transformational and servant leadership focus on inspiring and developing followers beyond mere task completion.
• Theoretical Frameworks, Major Exponents, and Contributions
o Max Weber:
Introduced the idea of formalized authority and bureaucracy.
o Frederick Taylor & Henri Fayol:
Laid the groundwork for scientific and administrative management principles.
o Kurt Lewin:
Pioneered studies on leadership styles and group dynamics.
o Fiedler, Burns, and Bass:
Developed contingency and transformational models emphasizing situational control and inspirational leadership.
• Dynamics of Group Behavior
o Group Processes:
Formation of norms, roles, cohesion, and communication patterns.
o Group Development Theories:
Tuckman's stages (forming, storming, norming, performing) illustrate the evolution of team dynamics.
o Impact of Leadership:
Leaders shape group behavior by resolving conflicts, fostering collaboration, and guiding decision-making.
• Theoretical Frameworks Supporting Group Behavior
o Social and Interaction Theories:
Lewin's work on group dynamics and Bales' Interaction Process Analysis help explain how groups maintain effectiveness.
o Leadership in Teams:
Research on leader-member exchange (LMX) shows how quality one-to-one interactions affect overall team performance.
• Comparing and Contrasting Types of Teams
o Functional Teams:
Comprised of members with similar skills working within one department.
o Cross-Functional Teams:
Include members from different functional areas, promoting diverse perspectives.
o Self-Managed Teams:
Operate with high autonomy and shared decision-making responsibility.
o Virtual Teams:
Rely on digital communication; require strong coordination despite physical dispersion.
Comparing and Contrasting Types of Teams
Virtual Teams
Rely on digital communication
require strong coordination despite physical dispersion
Self-Managed Teams
Operate with high autonomy and shared decision-making responsibility
Cross-Functional Teams
Include members from different functional areas
promoting diverse perspectives
Functional Teams
Comprised of members with similar skills working within one department
Theoretical Frameworks Supporting Group Behavior
Leadership in Teams
Research on leader-member exchange (LMX) shows how quality one-to-one interactions affect overall team performance
Social and Interaction Theories
Lewin's work on group dynamics and Bales' Interaction Process Analysis help explain how groups maintain effectiveness
Main topic
Dynamics of Group Behavior
Impact of Leadership
Leaders shape group behavior by resolving conflicts
and guiding decision-making
fostering collaboration
Group Development Theories
Tuckman's stages (forming
performing) illustrate the evolution of team dynamics
norming
storming
Group Processes
Formation of norms
and communication patterns
cohesion
roles
Theoretical Frameworks, Major Exponents, and Contributions
Fiedler, Burns, and Bass
Developed contingency and transformational models emphasizing situational control and inspirational leadership
Kurt Lewin
Pioneered studies on leadership styles and group dynamics
Frederick Taylor & Henri Fayol
Laid the groundwork for scientific and administrative management principles
Max Weber
Introduced the idea of formalized authority and bureaucracy
Comparing and Contrasting Leadership Theories
Modern Approaches
Transformational and servant leadership focus on inspiring and developing followers beyond mere task completion
Contingency/Situational Theories
Effectiveness depends on matching leadership style to situational factors (e.g
Fiedler's Contingency Model)
Behavioral Approaches
Analyze specific behaviors (e.g
'consideration')
Ohio State's 'initiating structure' vs
Classical Theories
Focus on management principles and efficiency (e.g
Weber's bureaucracy)
Types of Leadership and Leadership Styles
Servant/Distributed Leadership
Emphasizes follower growth
and collective decision-making
shared responsibility
Transformational
Inspires change through vision
and individualized support
charisma
Transactional
Based on exchanges (reward for performance
punishment for noncompliance)
Laissez-Faire
Leaders provide freedom for subordinates to manage their own tasks
Democratic/Participative
Leaders involve team members in decision-making
promote collaboration
Autocratic/Authoritarian
Centralized decision-making
minimal input from subordinates