jonka LeeAnn Fenlon 5 vuotta sitten
271
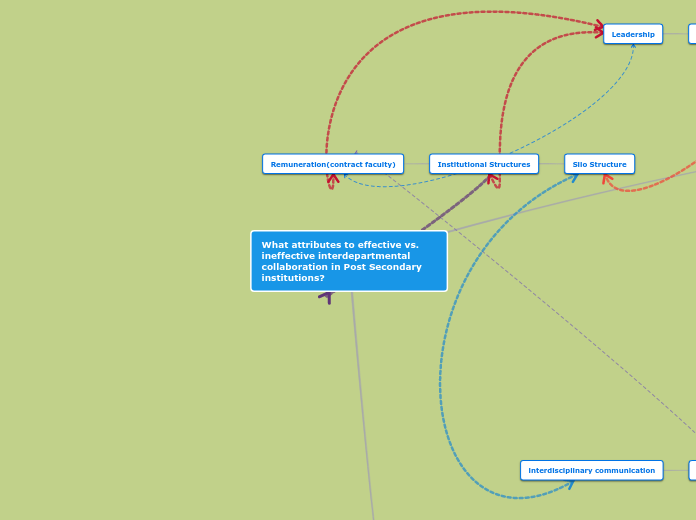
What attributes to effective vs. ineffective interdepartmental collaboration in Post Secondary institutions?
Effective interdepartmental collaboration in post-secondary institutions hinges on several key factors. Leadership plays a pivotal role in fostering a collaborative environment by promoting a culture that values teamwork and shared goals.