Psychedelics
LSD and Psilocybin are Schedule 1 Drugs and have a high potential for abuse. There is no accepted medial treamtent for these drugs in the US right not.
Intestinal muscle control
See people that are not there
Seeing things
Rapid mood swings
Hear sounds
Huffed
Drank
Common form
Psilocybin
Ketamine
Molly/Ecstasy
Mushrooms
LSD
Powder/Liquid
Eaten/drank
Snorted/Huffed
Memory loss
Vascular problems
Blindness
Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder
Severe anxiety
Hallucinations making you see things that are not there/not happening
Hallucinations leading to bad decision making
Impaired judgement
Headaches
Seizures
Nightmares
Flashback
Distorted sense of space/time
Enhance emotional empathy
Openness
Closeness to others
Change and enhance sensory perceptions, thought processes, energy levels and spiritual experiences.
Simulate and suppress the activity of neurotransmitters they are chemically similar to. This causes a chemical imbalance in the brain.
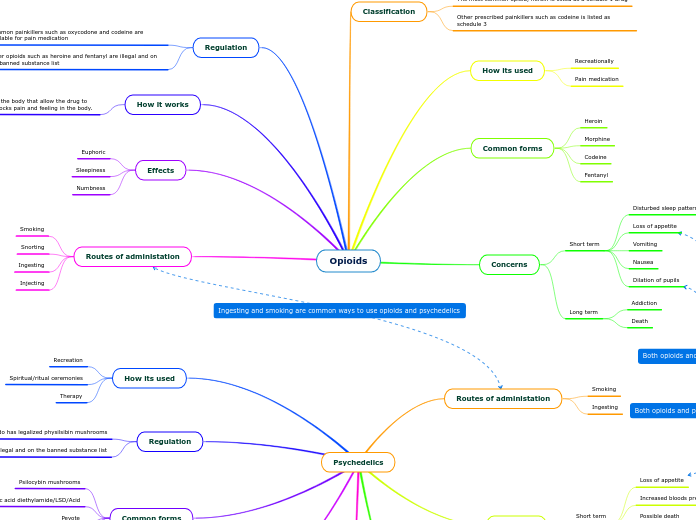
Opioids
Federal law states that opioids may be used for extended periods of time to treat patients with intractable pain.
Any use outside of the medial field is considered illegal for all ages in the United States.
As a drug (Heroin)
Medically
Relaxes body
relieves pain
Fully Synthetic
Tramadol
Methadone
Pethidine
Fentanyl
Semi-synthetic/Manmade
Hydromorphone
Heroin
Oxycodone
Hydrocodone
Natural
Thebaine
Codeine
Morphine
Routes of administration
Developing a tolerance
Liver damage
Abdominal distention
heart functions slow
Severe itching
Lethargy
Vomiting/Cold flashes
Muscle/bone pain
Restlessness
Dependence/addiction
Coma
Constipation
Drowsiness
Opioids act on opioid receptors in both the spinal cord and brain to reduce the intensity of pain-signal perceptions.
it also affects the brain areas control of emotion, which can further diminish the effects of painful stimuli and create relaxation or a "high" feeling.
Inhalants (Gases)
Sniffing/snorting or inhaling
Huffing (inhalant soaked rag stuffed in mouth)
Death by asphyxiation
Memory impairment
Disorientation
Muscle weakness
Death by suffocation
Heart failure
Severe headaches
Drunk apperance
Huffing
Bagging
Affects the nervous system rapidly as it is snorted/inhaled into the blood stream.
Inhalants slow down brain activity and produce the drunk like appearance and loss of consciousness.
Brain damage
Permanent nerve damage
Bone marrow damage
Hearing loss
Liver/Kidney damage
Prolong sniffing
Hostility
Lack of coordination
Slurred/distorted speech
Dilated pupils
Fatigue
Poor concentration
Inhalants are not regulated under the controlled substance act. However, the US has placed restrictions on the number of products that can be purchased per individual depending on the product.
Restrictions have also been set in place to prevent minors from accessing certain products.
House hold materials
Whipped cream aerosols or dispensers (whippets)
Propane tanks
Butane lighters
Methamphetamine
Snorting
Injection
Oral (medication)
Homicidal/Suicidal thoughts
Delusions/Paranoia
Psychotic behavior
Violent behavior
irritability/ confusion
irregular heartbeat
Increase productivity/alertness
Can cause a "rush"
Pills
Crystal meth (looks like crystals)
Crystalline powder
Increases the amount of natural chemical dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine is involved in the body movement, motivation, and reinforcement of rewarding behaviors, and meth allows high levels of it to be released.
Meth is illegal in the US except when give as a prescription.
The DEA classifies methamphetamine as a schedule II controlled substance, second highest classification there is.
Increased body temperatureregukre
Increased blood pressure
Rapid/ Irregular heartbeat
Decreased appetite
Increased physical activity
Long term
Damage to brain
Epilepsy
Stroke
Alzheimer's
Stron psychological dependence
Severe tooth decay
Liver/kidney damage
Short term
Convulsions/seizures
Disturbed sleep
Dilation of pupils
Loss of appetite
Snorted
Injected
Swallowed
Caffeine
Oral Ingestion
breathing tubes open up
Constriction of blood vessels
Slowing blood flow to stomach
Increased heart rate
Contraction of muscles
Insomnia
Nervousness
increased urination
fast heart rate
Tremors
Nervousness/Anxiety
High blood pressure
Dependency
Disrupted sleep
Upset stomach/Diarrhea
heartburn
irritability
Headache
Dehydration
When consumed, it stimulates the central nervous system, heart, muscles, and the centers that control blood pressure.
May also raise blood pressure and increase urine flow.
Caffeine is recognized as "safe"
No set age regulations.
Some regulations require that visible labels be displayed on items containing caffeine to prevent overconsumption.
Higher body temperature
Difficulty sleeping
Anxious
Refreshed
Eat it
Medications and prescriptions often contain caffeine
Chocolate is one of the most common forms of snacks
It is also widely craved by children
Coffee/energy drinks is the most common form of this
It may be used to subside headaches, improve asthma, athletic performance, and possibly reducing diabetes.
Prescription/ Non prescription medications.
Energy drinks
Chocolate
Soda
Hot chocolate
Tea
Coffee
Tobacco
Sniffing
Vaping/water-pipe
Chewing
Subtopic
Asthma
Osteoporosis
Addiction/Dependence
Lower fertility and increased risk of miscarriage
Heart disease
Cancer
high blood pressure
irregular periods
Shortness of breath
Loss of sense of smell/taste
eye cataracts
stomach ulcers
cancer
Teeth decay/tooth damage
Increased risk of stroke/brain damage
Bronchitis
Decreased lung capacity
Respiratory system damage
Absorbs into the blood stream when smoked, chewed, or sniffed.
Nicotine stimulates the adrenal glands an releases adrenaline. This also activates the brain's reward circuits and increases the levels of the chemical messengers dopamine.
Tobacco is available for purchase for individuals 21 years of age or older in every state but the following where it has been lowered to 18:
Virginia
Washington
Utah
Maine
Hawaii
Oregon
Massachusetts
New Jersey
Illinois
Delaware
California
Arkansas
Increased attention
Constricts blood vessels
Elevates blood pressure
Elevates heart rate
Sniffed
Snuff
Chewed
Snus
Chewing tobacco
Vape/E-Cigarette
Pipe/Hookah
Bidis
Cigars
Common Forms
Water-pipe/Hookah
liquid
Chew
loose leaf/fine cut
Cigarettes
leaf tobacco
Marijuana
Eating (edibles)
Vaping
Topicals
Bath salts
Lotion
Vaporized
E-cigarette
Vape pen
Smoked
Bong
Pipes/water pipe
Joints/blunts
Eaten
Candy
Ice cream
Burgers
Brownies
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), is the main chemical compound found in Marijuana.
When it enters the blood stream or is inhaled, it influences how the brain receptors communicate with the body. Giving people that "high" feeling.
May lead to dependence in other drugs
Other, more harmful, drugs
Drinking
Smoking
Increased agression
Lack of motivation in life
Impairs learning capabilities and performance.
Common forms
Concentrates
Hash/wax
Oils
Liquid
Marijuana (flowers and buds)
Stimulant
Elevated mood
Rapid heartbeat
Hallucinogen
Detachment from self
Loss of motor skills
Nausea
Dry mouth
short term memory loss
Sleepiness
Dizziness
Regulation
Marijuana is legal in but 10 US states for individuals 21 years old.
Decrease in IQ
Breathing problems
Financial difficulties
Possible addiction
Impaired ability to learn
Hallucinations
Altered motor skills/attention
Altered memory
Paranoia
Anxiety
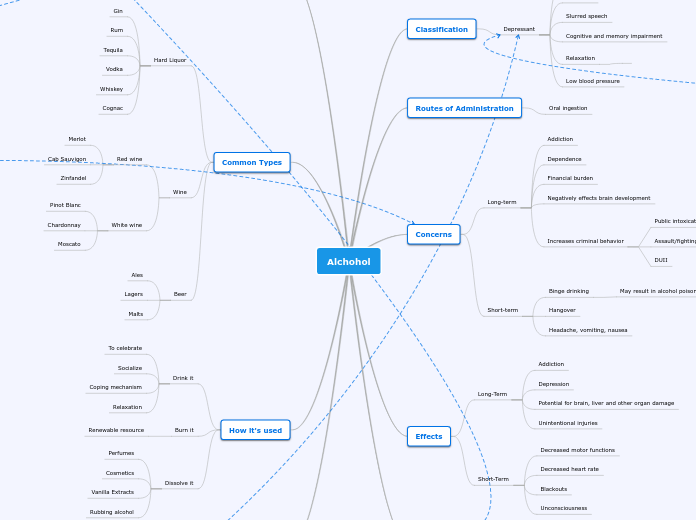
Alchohol
Main topic
How it's used
Dissolve it
Rubbing alcohol
Vanilla Extracts
Cosmetics
Perfumes
Burn it
Renewable resource
Drink it
Coping mechanism
Socialize
To celebrate
Common Types
Beer
Malts
Lagers
Ales
Wine
White wine
Moscato
Chardonnay
Pinot Blanc
Red wine
Zinfandel
Cab Sauvigon
Merlot
Hard Liquor
Cognac
Whiskey
Vodka
Tequila
Rum
Gin
Regulations
Must be 21 years of age in the United States to purchase.
Canada/Mexico is 18.
How it works
Alcohol can have a different affect on individuals based on their weight, age, and gender.
Once alcohol is consumed, it moves through the blood stream and affects the brain.
The liver then processes and metabolizes the alcohol and allows it to pass through the system.
Effects
Short-Term
Unconsciousness
Blackouts
Decreased heart rate
Decreased motor functions
Long-Term
Unintentional injuries
Potential for brain, liver and other organ damage
Depression
Concerns
Short-term
Headache, vomiting, nausea
Hangover
Binge drinking
May result in alcohol poisoning
Long-term
Increases criminal behavior
DUII
Assault/fighting
Public intoxication
Negatively effects brain development
Financial burden
Dependence
Addiction
Routes of Administration
Oral ingestion
Classification
Depressant
Low blood pressure
Relaxation
Cognitive and memory impairment
Slurred speech
Confusion
Impaired motor skills