This process occurs twice
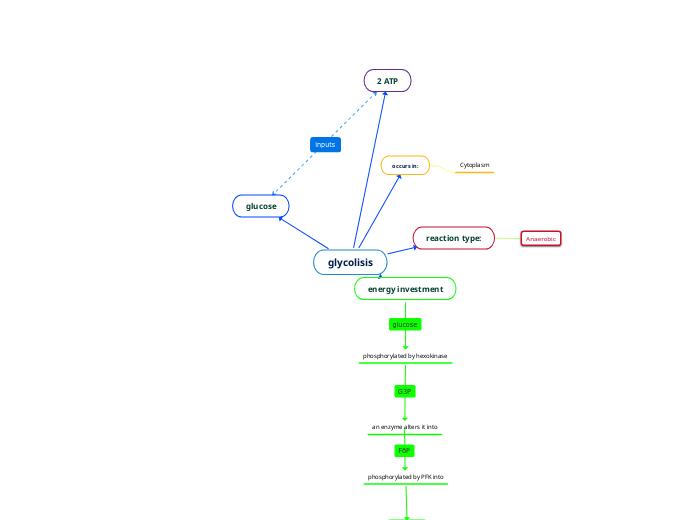
glycolisis
glucose
energy investment
phosphorylated by hexokinase
an enzyme alters it into
phosphorylated by PFK into
F16BP
BPG
3PG
2PG
PEP
Pyruvate
Pyruvate oxidation
Pyruvate enters mitochondria via transport protien
Pyruvate is decarboxylated and CO2 is released. It now has 2 carbons
Coenzyme A is attached to make acetyl CoA
Acetyl CoA
Krebs Cycle
Oxidative phosphorylation
2 steps
Chemiosmosis
Pumps protons from inner membrane back down the H+ gradient which results in the making of ATP through ATP synthase
ATP Synthase
transport protien
As protons move down the gradient ADP is turned into ATP
Production of ATP is called oxidative phosphorylation
Final step of Cellular respiration
Electron Transport Chain
FADH2
goes through complexes 2,3,4
6 protons
1.5 ATP
NADH
goes through complexes 1, 3, 4
10 protons
2,5 ATP
Complex I
Intermembrane space
Complex II
Coenzyme Q
Complex III
Cytochrome C
Complex IV
Oxygen( HEATHER)
Oxygen is the most electronegative, it drives ETC as well as removes electrons from complex IV and 2 protons from the matrix ( this makes H2O
Electrons are delivered by NADH and FADH2
proton pumping
Splitting of oxygen to form H2O
movement of electrons
electrochemical gradient
NAD+ and FAD
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Oxaloacetate
NAD= into NADH
Cirate
Isocitrate
a- ketoglutarate
Succinyl- CoA
Coenzyme A is added
Succinate
Fumarate
Malate
H2O
FAD into FADH2
CoA
ATP
NAD+ to NADH
NAD+ into NADH
Co2
Co2 and H2O
per glucose
matrix of the mitochondria
Aerobic
NAD+ is reduced to NADH
aerobic
End products:
ONLY 2 NET ATP
4 ATP
DHAP
G3P
reaction type:
Anaerobic
occurs in:
Cytoplasm
2 ATP