Chapter 3 (Continued)
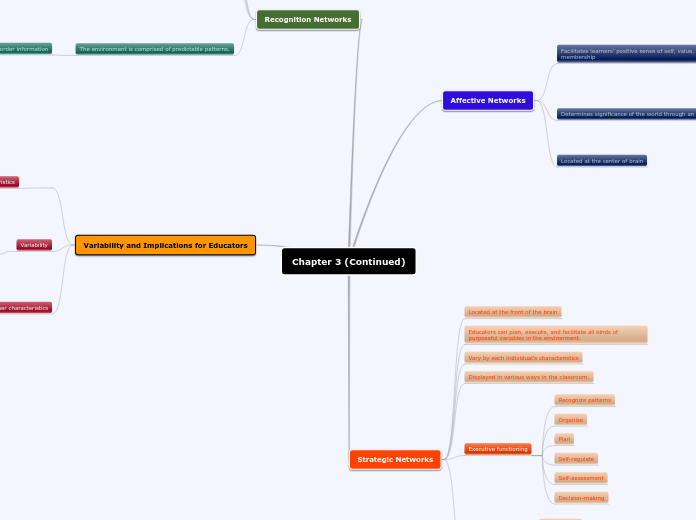
Variability and Implications for Educators
Former beliefs of learner characteristics
Variability is a liability
Some of these misconceptions are still present today
Education could improve learner abilities but not brain and genes
Learners were limited to their biological composition (brains and genes)
labeled - intelligent, average, dull
Variability
Combination of strengths and challenges that a learner is made up of.
Recognition Networks
The environment is comprised of predictable patterns.
Facilitate recognition of higher-order information
higher-order information
Patterns
individual aspects of patterns, such as their color, shape, orientation, or motion are processed by separate parts of recognition networks.
What the learner sees, hears, smells, tastes, and touches
Context
Experience
Background
Varies from person to person
Systematic variability is anticipated from the outset.
recognition systems intensely interconnected
located in the back of the brain
Strategic Networks
Strategic action
Reflect - correct/adjust
Self-monitor
Initiate plan
Design plan
Identify goal
Executive functioning
Decision-making
Self-assessment
Self-regulate
Plan
Organize
Recognize patterns
Displayed in various ways in the classroom.
Vary by each individual's characteristics
Educators can plan, execute, and facilitate all kinds of purposeful variables in the environment.
Located at the front of the brain
Affective Networks
Located at the center of brain
Determines significance of the world through an affective filter
Inhibits emotional responses
Understanding emotions can impact student learning
stressful and/or fearful situations
Interpreting/creating our own reality
Prioritize actions
what we do and learn
Facilitates learners’ positive sense of self, value, and membership
Increased performance
Positive impact on learning