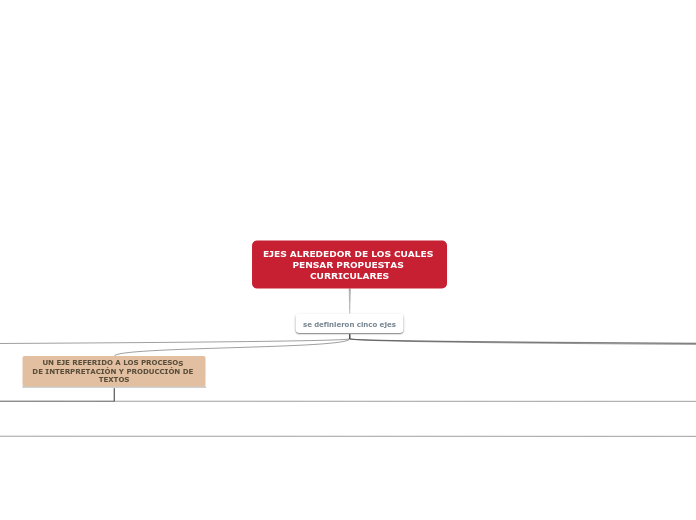
EJES ALREDEDOR DE LOS CUALES PENSAR PROPUESTAS CURRICULARES
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
se definieron cinco ejes
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
UN EJE REFERIDO A LOS PRINCIPIOS DE LA INTERACCIÓN Y A LOS PROCESOS CULTURALES IMPLICADOS EN LA ÉTICA DE LA COMUNICACIÓN
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
DIVERSIDAD ÉTNICA Y CULTURAL
se encuentran una
BILINGÜISMO
ENSEÑANZA EQUILIBRADA
LENGUA MATERNA
y el
CASTELLANO
DIVERSIDAD LINGÜÍSTICA
COLOMBIA
tenemos
64 LENGUAS INDÍGENAS
por esto en las
INSTITUCIONES EDUCATIVAS
deben ser
ENSEÑADAS
DIFUNDIDADAS
con el mismo
ESTATUS SOCIAL
de cualquier otra
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
PROCESO ASOCIADO
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
reconocimiento
MÚLTIPLES CÓDIGOS
LINGÜÍSTICOS
CULTURALES
CIRCULAN
AULA
TURNOS CONVERSACIONALES
RESPETO DE ROLES
SOCIALES
PRINCIPIOS BÁSICOS
de la
desde
CREACIÓN
RESPETO
por la
DIVERSIDAD CULTURAL
UN EJE REFERIDO A LOS PROCESOS DE DESARROLLO DEL PENSAMIENTO
ESTRATEGIAS METACOGNITIVAS PARA MEJORAR LA COMPRESIÓN LECTORA
ESTRATEGIAS PARA EL APRENDIZAJE DE INFORMACIÓN
esta dividido
TRES FASES
TERCERA
se orienta a la
REGULAR
PROPIA LECTURA
tales como la
AUTOCONOCIMIENTO
RECLECTURA
EVALUAR
SEGUNDA
comprede el
ESTRATEGIAS ESPECIFICAS
relacionadas con la
IDENTIFICACIÓN
IDEAS PRINCIPALES
PRIMERA
dirige la
ENSEÑANZA
ASPECTOS GENERALES
PLANES
consiste en
TOMAR
conciencia del
PROPIO PORCESO
de manera que el
pueda
SUPERVISAR
CONTROLAR
ESTRATEGIAS COGNITIVAS PARA FACILITAR LA COMPRENSIÓN TEXTUAL
elementos
TEÓRICOS
deben promoverse
para el
DESPUÉS DE LA LECTURA
REDES CONCEPTUALES
permite
PROCESO COGNITIVO
GRÁFICO PERCEPTIVO
PARAFRASEO
trata de
con sus
PROPIAS PALABRAS
COMPRENDIO
RELECTURA
DISCUSIÓN
sobre lo
COMPRENDIDO
en la
TÉCNICAS DEL RECUENTRO
sobre
COMPRENDIERON
facilita la
RECONSTRUCCIÓN
ANTES Y DURANTE LA LECTURA
COMENTARIOS PREVIOS
EL TITULO DEL TEXTO
y sus
IMÁGENES
o
HABLAR
sobre el
ESCRIBIR
no
FRAGMENTAR
RELACIONA
LEGUAJE
DESARROLLO DEL PENSAMIENTO
UN EJE REFERIDO A LOS PROCESOS CULTURALES Y ESTÉTICOS ASOCIADOS AL LENGUAJE: EL PAPEL DE LA LITERATURA
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
RECAPITULACIÓN
no como la
ACUMALCIÓN
INFORMACIÓN GENERAL
sino la
y de
dela
ARGUMENTACIÓN CRÍTICA
EL DIALOGO ENTRE LOS TEXTOS:
UNA POSIBILIDAD DE TRABAJO CON LA LITERATURA
depende de la
CRÍTICA
un saber proponer
INTERPRETACIONES
esta en
PROFUNDA
implica un
que va desde el
NIVEL
CRITICO INTERTEXTUAL
va operado en un
LECTOR COMPETENTE
se caracteriza porque se
GENERAN
RELACIONES DIALÓGICAS
DIVERSAS CLASES
y no solo
LITERARIOS
SECUNDARIO O LECTURA INFERENCIAL
PRIMARIO O LECTURA LITERAL
en
PROFUNDIDA
LITERARIA
entendida desde el
CONOCIMIENTO DIRECTO
NÚMERO DE OBRAS
es un saber
LITERARIO
que ha
SURGIDO
desde la
EXPERIENCIA
se manifiestan
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
TRES ASPECTOS
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
LITERATURA
ÁMBITO TESTIMONIAL
en que el
IDENTIFICAN
MOMENTOS HISTÓRICOS
OBRAS
AUTORES
RAGOS DE LA ORALIDAD
TENDENCIAS
en estas
DIMENSIONES
se encuentran
PARADIGMAS
desde los cuales
PROFUNDIZAN
ESTUDIO
siendo desde la
SEMIÓTICA
HISTORIOGRAFÍA
SOCIOLOGÍA
ESTÉTICA
CONVERGENCIA
MANIFESTACIONES HUMANAS
ARTES
CIENCIA
REPRESENTACIÓN
SUSCITACIÓN
de lo
ESTÉTICO
UN EJE REFERIDO A LOS PROCESOS
DE INTERPRETACIÓN Y PRODUCCIÓN DE TEXTOS
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
CONCEPTUALIZACIÓN DEL PROCESO LECTOR
para tener una
EDUCACIÓN DE CALIDAD
se necesitan unas
COMPETENCIAS
que faciliten la
CULTURA
CINENCIA
estos son
CONCEPTO DE LA LECTURA
el cua es un
PROCESO
CONSTRUCCIÓN
a partir de la
INTERACCIÓN
entre el
existen
TRES TIPOS
PSICOLÓGICO
se refiere al
ESTADO ANÍMICO
en el
MOMENTO
LEER
compuesto por
como el
ESPACIO FÍSICO
donde se realice la
afectan la
COMPRESIÓN TEXTUAL
CLIMA
esta
REPRESENTADO
por las
presentes
DESPUÉS
ENUNCIADO
ANTES
REGLAS
para elaborar
según
CASSANY
CORRECIÓN GRAMATICAL
alude al
CONOCIMIENTO FORMAL
donde se
INCLUYEN
CONOCIMIENTOS GRAMATICALES
MORFOSINTAXIS
FONÉTICA
COHESIÓN
ordenar
como se
CONECTAN
ENLAZAN
COHERENCIA
RELACIONADA
con el
ORDEN LÓGICO
PRESENTA
ADECUACIÓN
PROPIEDAD DEL TEXTO
DETERMINA
INTENCIÓN COMUNICATIVA
se identifican diferentes
REDACIÓN
VOCABULARIO
se identifican
TRES COMPONENTES
son
CONSISTENCIA INTERNA
LECTURA INTEGRADA
CONSISTENCIA EXTERNA
EL LÉXICO
PRESICIÓN
CLARIDAD
CONTENIDO
LECTOR
diversos
permiten
FACILITAR
COMPRESIÓN DEL LECTOR
entre ellas se encuentran
ESTRATEGIAS
AUTO CORRECCIÓN
VERIICACIÓN
INFERENCIA
concluir
acerca de los
deducir
PREDICCIÓN
que posee el
ANTICIPAR
CONTENIDOS
ademas permite
HIPÓTESIS
relacionadas con el
DESARROLLO
y
FINALIZACIÓN
estas son
ESTRATEGIAS BÁSICAS
en las que se
CONSTRUYE SIGNIFICADOS
también se
CONSIDERAN
otros
FACTORES
que son
COMPETENCIAS DE LENGUAJE
se trata de
CONO-CIMIENTO
que el
LEYENTE
posee de su
LÉXICO
hace referencia a la
COMPETENCIA
GRAMATICAL
SEMÁNTICA
TEXTUAL
SITUACIÓN EMOCIONAL
entre la
REALIDAD INTERIOR
REALIDAD EXTERIOR
en la que
HABILITA
REALIDAD AFECTIVA
condicionan la
NIVEL DEL DESARROLLO COGNITIVO
INDIVIDUO
poder
ASIMILAR
lo que
SIGNIFICA
es
NECESARIO
aplicar los
ESQUEMAS
disponibles
PARA
RESOLUCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS
que se
PRESENTEN
CONOCIMIENTO PREVIO
es el
GRADO
COMPRESIÓN LECTORA
determinada por
PROPÓSITOS
se
REFIERE
a la
CONCIENCIA
LEE
con un
FIN
que soN
CONDICIONES
MUESTREO
que pose el
para seleccionar
COGNITIVAMENETE
IDEAS
más
SIGNIFICATIVAS
PALABRAS
VIDA
constituye un
NIVEL MACROESCTRUTURAL
CATEGORÍA PARA EL ANÁLISIS DE LA PRODUCCIÓN ESCRITA
se divide en cuatro niveles
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of viewSecond person point of viewThird person point of viewOmniscient point of view
esta configurada por dos
CATEGORÍAS
SUPERESCTRUCUTRA
POSIBILIDAD
SELECCIONAR
y seguir un
PRINCIPIO LÓGICO
ORGANIZACIÓN
MISMO
INTENCIÓN
CAPACIDAD
de responder a un
REQUERIMIENTO
a través de un
TIPO DE TEXTO
se refiere a la
atendiendo a una
INTENCIONALIDAD
sieno un
LENGUAJE PERTINENTE
COHERENCIA Y COHESIÓN LINEAL
establecimientos de
JERARQUÍAS
RELACIONES
entre las
para construir
MAYOR SIGNIFICADO
VÍNCULOS
seguimiento de un
NÚCLEO TEMÁTICO
a lo largo de la
constituye un nivel
MAROESCTRUCTURAL
COHERENCIA Y COHESIÓN LOCAL
es la realización
ADECUADA
ENUNCIADOS
NIVEL MICROESCTRUCTURAL
es decir
PROPOSICIONES
se entiende el
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
TEXTO
un
TEJIDO
SIGNIFICADOS
que
OBEDECE
unas
REGLAS ESTRUCTURALES
SINTÁCTICAS
para la
PRODUCCIÓN
ANALISIS
DIVERSOS TIPOS DE TEXTOS
se consideran
TRES TIPOS DE PROCESOS
EXTRATEXTUAL
se constituye por el modelo
PRAGMÁTICO
es el encargado del
CONTEXTO
significa que es la
SITUACIÓN
COMUNICACIÓN
en la que se dan
ACTOS
HABLA
INTERTEXTUAL
su componente es
RELACIONAL
porque se ocupa de las
RELACIONES CON OTROS TEXTOS
se entienede como
CONTENIDOS O INFORMACIONES
presentes en un
TEXTOS
que provienen de
OTRO
INTERATEXTUAL
se estructura por
PRESENCIA
SINTÁCTICO
SUPERESCTRUTURAS
es la forma global como se
ORGANIZAN
COMPONENTES
LÉXICOS
son los
CAMPOS SEMÁNTICOS
SEMÁNTICOS
MACROESCTRUCUTURAS
COHERENCIA GLOBAL
que tiene una
PROPIEDAD SEMÁNTICA GLOBAL
haciendo un
SEGUIMIENTO
de un
EJE TEMÁTICO
a lo
LARGO DEL TEXTO
MICROESTRUCTURAS
se entiende como
ESTRUCTURA
de las
ORACIONES
y la
entre ellas
COHERENCIA LINEAL
entendida como
ILACIÓN
SECUENCIAS DE ORACIONES
a través de
RECURSOS LINGÜÍSTICOS
COHERENCIA LOCAL
CONCORDANCIA
NÚMERO
GÉNERO
VERBO
SUJETO
COMPRESIÓN
SEMÁNTICAS
UN EJE REFERIDO A LOS PROCESOS DE CONSTRUCCIÓN DE SISTEMAS DE SIGNIFICACIÓN
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
hace referencia al
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
se definieron cinco ejes.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
CONJUNTO
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
de
LENGUAJES DE LAS IMAGENES
LENGUAJE VERBAL
CONTEXTOS DE USO EN GENERAL
en este eje se encuentran
CUATRO NIVELES
TRABAJO PEDAGÓGICO
los cuales son
está referido a la
TOMA
REGULACIÓN
SISTEMAS DE SIGNIFICACIÓN
FINALIDADES
SIGNIFICATIVAS DETERMINADAS
COMUNICATIVAS
DISTANCIA
EXPLICACIÓN
su
OBJETO DE ESTUDIO
es la
LENGUA
en este caso la
PRAGMÁTICA
SINTAXIS
ORTOGRAFÍA
encuentran su
LUGAR
como
HERRAMIENTAS
FUNCIONA
el
LENGUAJE
explicar
LINGÜÍSTICA
TEORÍA GRÁMATICAL
RELACIONADO
con la
REFLEXIÓN SISTEMÁTICA
sobre los
FUNCIONAMIENTOS
de los
SISTEMAS
USO
SISTEMA
FINES
SIGNIFICATIVOS
COMUNICATIVOS
la
ESCUELA
debe
OCUPARSE
de trabajar
SISTEMÁTICAMENTE
las
HABILIDADES
para
producir
diferentes
TIPOS DE TEXTOS
comprender
está
ASOCIADO
con las
PRÁCTICAS
LENGUAJE DE IMÁGENES
ORALIDAD
LECTURA
UN NIVEL DE CONSTRUCCIÓN O ADQUISICIÓN DEL SISTEMA DE SIGNIFICACIÓN
los
NIVELES DE CONSTRUCCIÓN
del
SISTEMA DE ESCRITURA
por el
NIÑO
describiendo
TRES NIVELES
TERCERO
se presentan
TRES HIPÓTESIS
ALFABÉTICA
SILÁBICO ALFABÉTICA
SILÁBICA
aparece la
SONIDO -GRAFÍA
es decir la
REPRESENTACIÓN ESCRITA
SEGUNDO
se trabaja el
SIGNIFICADO
de la
PALABRA
aun no hay
RELACIÓN
con
SONIDO-GRAFÍA
aparece un
CONTROL
sobre la
CUALIDAD
CANTIDAD
PRIMERO
hay una
DISTINCIÓN
entre
siendo
GRAFÍAS
DIBUJO
LENGUAJE ICONO
garantiza el
APROPIACIÓN DEL SISTEMA
CONOCIMIENTO
RECONOCIMIENTO
el manejo del
CÓDIGO ALFABÉTICO CONVENCIONAL
es un
PUNTO DE LLEGADA
por esto es necesario
GENERAR ESPACIOS
SIGNIFICACIÓN
en donde la
CÓDIGO ALFABETICO
será una
NECESIDAD
que aparecerá de
MANERA NATURAL
FONETIZACIÓN
ESCRITURA
cobre
SENTIDO SOCIAL
PRAGMÁTICAS
REGLAS SINTÁCTICAS
SIMBOLOS
SIGNOS
de las diferentes
FORMAS
de las cuáles se
CONSTRUYE