par Chaco Chaco Il y a 4 années
292
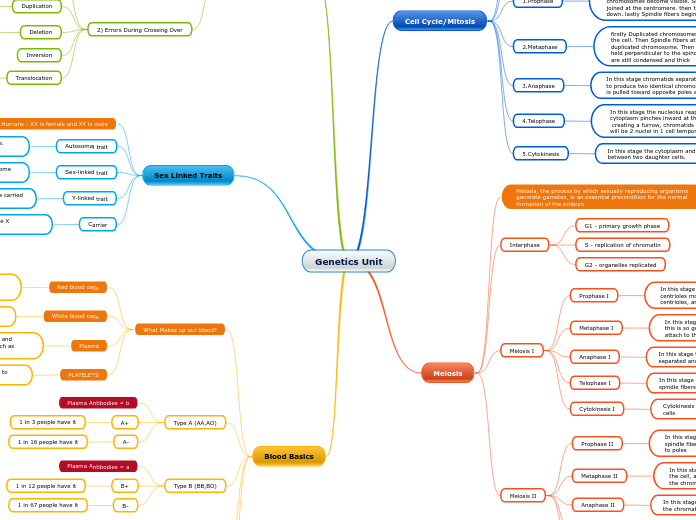
Genetics Unit
par Chaco Chaco Il y a 4 années
292

Plus de détails
Type in the name of the company you are going to have an interview with.
How ambitious are you?
1 in 15 people have it
1 in 167 people have it
1 in 29 people have it
1 in 67 people have it
1 in 12 people have it
1 in 16 people have it
1 in 3 people have it
these are tiny blood cells that help your body form clots to stop bleeding.
This part of the blood contains electrolytes, nutrients and vitamins, hormones, clotting factors, and proteins such as antibodie.
Are part of the immune system and help protract us from infections and diseases.
This cell is the most abundant cells in our blood. They are produced in the bone marrow and have a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen to our cells.
Why will/did you leave your existing/last job?
Do you fully understand what this position implies?
After you've made some research on the company, read the job description thoroughly, and try to fully understand what your responsibilities will be.
Results in a Gene not being able to be expressed properly
Results in a loss of genetic information
Results in an extra copy of the gene
Results in Down Syndrome
Results in Klinefelter Syndrome
Results in Turner’s Syndrome
Are you qualified for this position?
Interviewers will want to know whether or not you are able to do the job.
Answer the questions from this section and see if you are the right person for this position.
Four genetically different daughter cells form
In this stage the Nuclear membrane reassembles, chromosomes decondense, and the spindles disappear
In this stage the spindle fibers pull the chromatids apart
In this stage the chromosome pairs align along the equator of the cell, and then the Spindle fibers attach to centromeres of the chromatids
In this stage the nuclearmembrane begins to break down, spindle fibers begin to form, and the centrioles begin to move to poles
Cytokinesis occurs forming two genetically different daughter cells
In this stage the nuclear membrane reforms and the spindle fibers retract.
In this stage the chromosome pairs are separated and are pulled to opposite ends
In this stage the tetrads line up along the equator randomly this is so genetic variation can occur, then the spindle fibers attach to the pair of sister chromatids
In this stage Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centrioles move to opposite poles, spindle fibers form from centrioles, and the nuclear membrane breaks down
Research the company
You should find and learn as much as you can about the company where you are having an interview.
The interviewer will want to see what you know about them and why you chose the company.
Doing your homework will show that you are really interested.