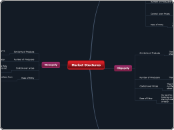
Market Stuctures
Monopoly
Ease of Entry
There is a high barrier to entry, it limits others from entering.
Control over prices
The usually have a good control over prices, because they control the supply and demand. They are price setters not price takers.
There is only one producer in a monoply.
In a monoply their products are very unique because they're one of a kind. No other producer has it.
Monopolistic Competition
Its usually easy to become a part of this market because the start up cost are usually low.
They usually have some control over the prices because its their brand.
Number of Producers
There are many producers in a monopolistic competition.
Similarity in Products
In this type of market there is product differentiation, seeking to distinguish their good and services from other firms.
Oligopoly
Its hard for a new firm to come into a oligopoly due to keeping up with other businesses. One reason is because of the high cost becasue others have large investments already.
Control over Prices
They have some control over prices because of the small number of firms, its usually based on the price decsions of other firms.
There are only a few number of firms in an oligpoly
Similarity of Products
They have similar products with few minor difffereces like shape and size.
Subtopic
Perfect Compition
Ease of Entry
There is an easy entry into the market, becasue they're such few resrtictions to the market.
Control over Prices
No control over prices: Under the condition producers have no market power. Cannot influence prices because there are too many others with the same products. Price takers mict accept, or take the market price for their product.
Number of Producers
Many number of producers and consumers, having a large number of participants in a market help promote competition.
Similarity of Produces
Virtually identiacal. A product that is excalty the same no matter the producer is called a "commodity".
Ex: Grain, cotton, sugar, and crude oil.