Introduction to Psychology
Psychology as a Research Science
Empirical Method
Scientific Method
Hypothesis Testing
Qualitative research,
Quantitative research
Ethnographic research
Chimpanzee studies
(Jane Goodall)
Observation vs. Participation
Observer effects
Observer bias
Correlational research
Direction of causation
Confounding variables
Positive vs. Negative correlation
Survey research
Experimental research
Sampling
Random assignment
Placebo Effect
Controlled experiments
Dependent variable,
Independent variable,
Single, Double blind experiments
Health, Stress, Coping
Happiness
Death salience
The Surprising Ways Death Shapes Our Lives - YouTube
Relationship between money and happiness
Mindfulness
Gratitude
Habits, Rituals
Social relationships
Delayed gratification
Future vs. Present self
Coping
5 stages of grief/loss
(Kubler-Ross)
Optimal performance
Exercise, sleep
Flow
Normal vs. "Abnormal"
Psychological Disorders
Neuroscience
Memory
Amnesia
False memories
Short-term memory,
Long-term memory,
Working memory
Sensation, Perception
Illusions
Sensory adaptation
Signal detection
Sensitization vs. Desensitization/habituation
Threshold of perception
5 senses
Endocrine System
Glands
Hormones
Nervous System
Neurons
Neuroplasticity
How drugs work
Neurotransmitters
Central nervous system,
Peripheral nervous system
Parts of the brain
Case of Phineas Gage
(brain damage)
Society and Culture
Family
Warm vs. Cold
(Harry Harlow)
Family origins
Group dynamics
Schemas
Social identity
Sterotypes,
heuristics,
discrimination,
implicit biases
Contact hypothesis
Conformity
Social Norms
Bystander Effect
Kitty Ge
Individualism, Collectivism
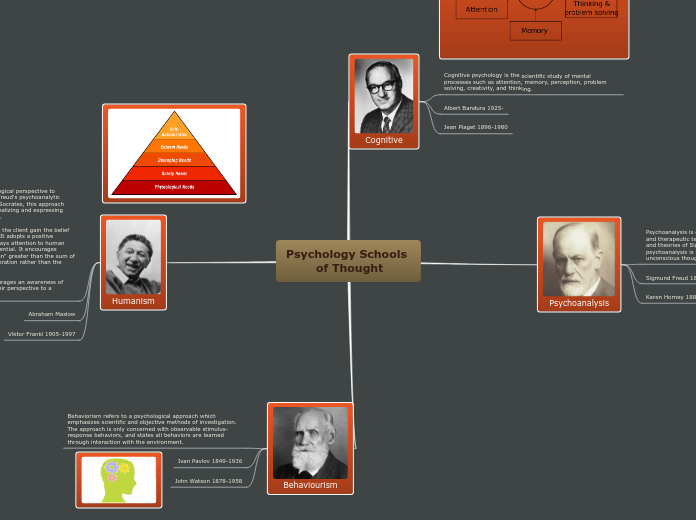
Major Schools of Psychology
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive biases
Knowledge, facts, opinions, fake news
Conspiracy theories
Internal attribution,
External attribution
Intelligence
Different kinds of intelligence
IQ Testing
Life Development
Nature vs. Nurture
Reaction range
Zone of Proximal Development
(Lev Vygotsky)
4 Stages of Cognitive Development in Children
(Jean Piaget)
Deductive Reasoning
Conservation
Object Permanence
Egocentrism
Humanistic Psychology
Social Emotional Learning
Self-reflection, introspection
Self-awareness
Johari Window
Blindspots
Motivation
Learned Helplessness
(Martin Seligman)
Maslow's Hierarchy
Fixed Mindset vs. Growth Mindset
Hertzberg’s 2-Factor Theory:
Hygiene factors,
Motivating factors
Relationship between money and motivation
McClelland’s Theory of Needs:
Achievement,
Affiliation,
Power
Behavioural Psychology
Psychodynamic Psychology
Models of Personality
16 Personalities (MBTI)
Big 5 Personality Traits (NEO-PI)
Conscious, Subconscious, Unconscious
Id/Ego/Super Ego
Defense Mechanisms
(Freud)
Main topic
How we communicate
Pursuasion
Storytelling
Communication Theory
Feedback
Non-violent communication (Rosenberg)
Miscommunication
How we learn
Social Learning Theory
Socialization
Bobo Doll experiments
(Albert Bandura)
Operant Conditioning
Schedules of Reinforcement
Antecedent,
Behaviour,
Consequence (ABC)
Rats in a box
(BF Skinner)
Positive/Negative Rewards/Consequences
Classical Conditioning
Stimulus-response association
Case of Little Albert
(John B. Watson)
Salivating dogs (Ivan Pavlov)