Form & Function
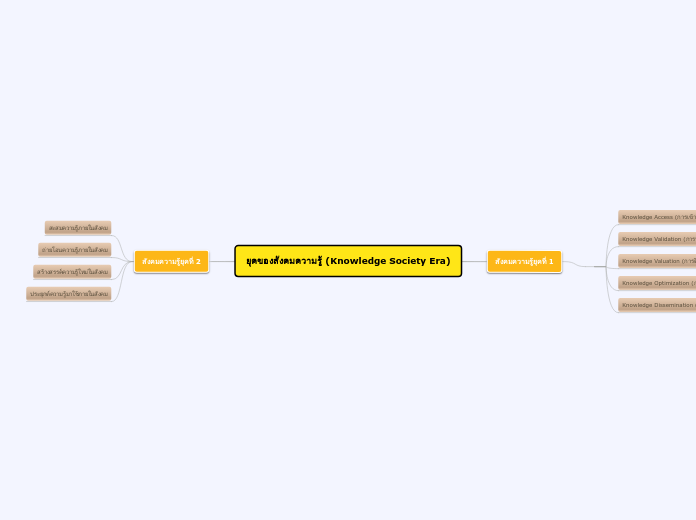
Magnitude and Direction of Force
Magnitude
Magnitude is how forces are measured, seeing as a force with a high magnitude is a powerful force, and one with a low magnitude is a weak force. Magnitude is also shown by how long an arrow is in diagrams.
Direction of Force
The direction of force is simply the way that the force is pushing, pulling, twisting or shearing
Point and Plane of Application of Force
Where forces are hitting a structure is called the point of application, and the imaginary line the force is passing through is called the plane of application.
Design Features
Design features are things in the design of structures that make it stronger, more durable, or to make it look better.
External & Internal Forces
External Forces
Dead Load
A dead load is a constant load on a structure
Live Load
A live load is a moving, variable weight added to the already existing weight of a structure
Internal Forces
Types
Compression
Compression is the action or state of being squished down or made smaller or more pressed together.
Torsion
Torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied force
Tension
Tension is the pulling force exerted by each end of a string, cable, chain, or similar one-dimensional continuous object, or by each end of a rod or similar three dimensional object.
Shear
Shear is a map of a coordinate space in which one coordinate is held fixed and the other coordinate or coordinates are shifted.
Center of Gravity & Stability
Center of Gravity
The center of gravity is the place in a system or body where the weight is evenly dispersed and all sides are in balance.
Stability
Stability is the state of being resistant to change or, just the state of being stable.
Types of Structures
Frame Structures
A framed structure in any material is one that is made stable by a skeleton that is able to stand by itself as a rigid structure without depending on floors or walls to resist deformation.
Shell Structures
Structures, which keep their shape and support loads, even without a frame, or solid mass material inside, are called shell structures. These structures use a thin, carefully shaped, outer layer of material, to provide their strength and rigidity. The shape of a shell structure spreads forces throughout the whole structure, which means every part of the structure supports only a small part of the load, giving it its strength.
Subtopic
Mass Structures
Facts
Can be made by piling up or forming similar materials into a particular shape or design. Mass structures also are not always solid, but are layered and have hollowed out areas for specific functions, such as as dams, walls or maybe monuments
Examples