par Brenda Mitchell Il y a 5 années
441
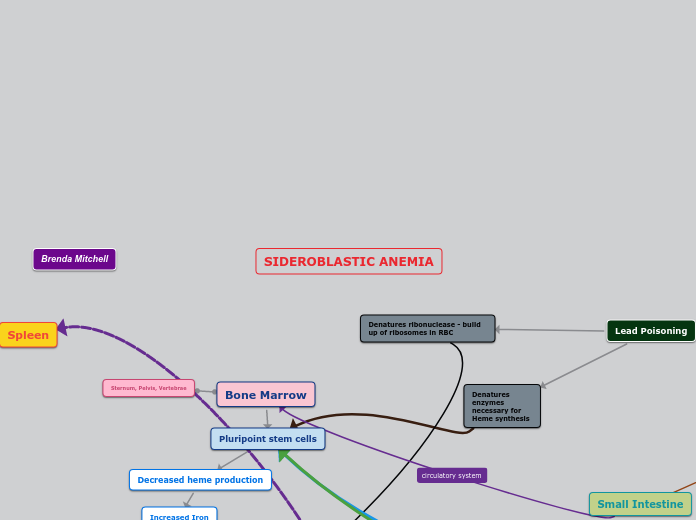
SIDEROBLASTIC ANEMIA
A specific type of anemia, known as sideroblastic anemia, involves several key issues related to iron metabolism and heme synthesis. It is characterized by the presence of ringed sideroblasts in the bone marrow and can result from enzyme denaturation due to lead poisoning or vitamin B6 deficiency.