par Natalie Mammone Il y a 4 années
783
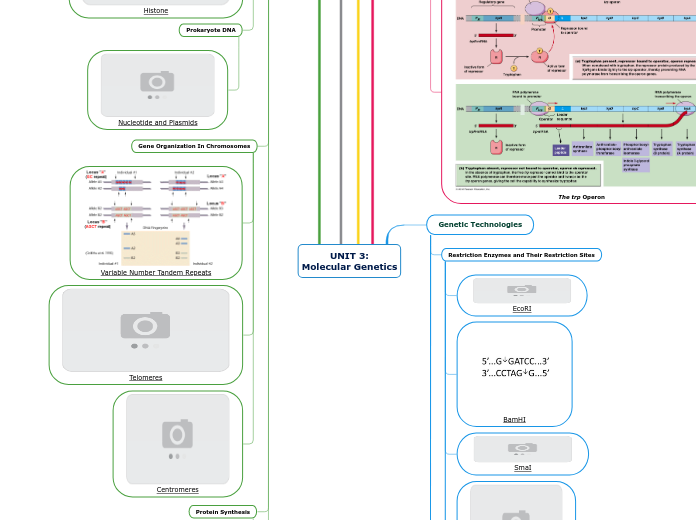
UNIT 3: Molecular Genetics
DNA replication is a critical process that involves unwinding the double helix and synthesizing complementary strands. This process can occur through conservative, dispersive, or semiconservative methods, with key enzymes like DNA helicase playing vital roles.