Analysis Connections
Titration
Solutions
Solute
Purity
Ph
Solvent
Aqueous
Stoichiometry
The Mole
Avogadro's Number
Density
Archimedes Principle
Molar Mass
Empirical Formula
Reactions
Concentration
Concentration is the ratio of solute in a solution to either solvent or total solution.
Concentration Formula: M = N/V
Precipitation and Selective Precipitation
Reagents
Limiting Reagents
The reactant that is used up completly in a reaction is called a limiting reagent. They are substances that are completely used up in the completion of a chemical reaction.
Anions
Larger
Negative
Gain Electrons
An anion is as an atom that is negatively charged
Cations
An cation is an atom or molecule that is positively charged
Positive
Loose Electrons
Smaller
Paper Chromatography
Pure Substances
Elements
Nobles gases
Metalloids
Metals
Non-Metals
Compounds
Mixtures
Heterogeneous
Homogenous
A mixture is composed of one or more pure substances in varying composition
A small spot of a soluble mixture is placed on the paper. The solvent carries a mixture up the paper. Different components of the mixture have different relative affinities to the stationary and mobile phases and so travel up the paper at different speeds. This separates the components.
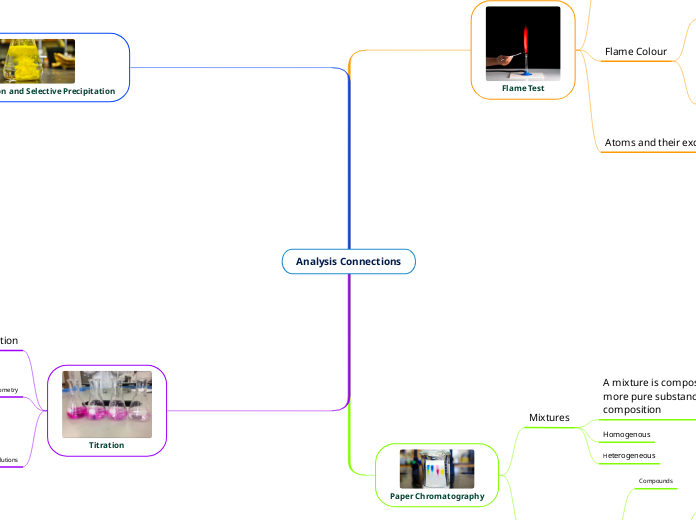
Flame Test
Atoms and their excited state
An atom or ion is excited by heating it to high temperatures, the electrons are promoted from their normal unexcited state into higher orbitals.
Higher Potential energy
Flame Colour
Emmison spectra
the emission spectrum is used to identify different elements
Flame
Size
Duration
Colour