Chapter 2 - Anatomical Bases of Human Motion
Qualiative Analysis
Visual observation is the most commonly used approach.
Conducting The Analysis
Planning
Background
Lighting Conditions
PerformerAttire
Prerequisite Knowledge
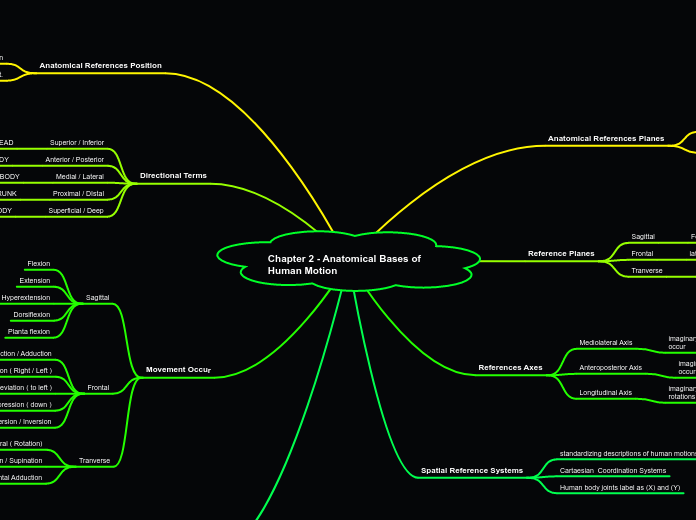
Movement Occur
Horizontal Abduction / Horizontal Adduction
Pronation / Supination
Medial / Lateral ( Rotation)
Eversion / Inversion
Foot print inside / outside
Elevation ( up ) / Depression ( down )
Shoulder
Radial Deviation ( to left ) / Ulnar Deviation ( to left )
Wrist
Lateral flexion ( Right / Left )
Upper body
Abduction / Adduction
Leg to inside / outside
Planta flexion
Dorsiflexion
Hyperextension
Extension
Flexion
Directional Terms
Superficial / Deep
SURFACE OF BODY
Proximal / DIstal
TRUNK
Medial / Lateral
MIDLINE BODY
Anterior / Posterior
BODY
Superior / Inferior
HEAD
Anatomical References Position
Considered all segments of body movement.
Facing foward on standing position
Spatial Reference Systems
Human body joints label as (X) and (Y)
Cartaesian Coordination Systems
standardizing descriptions of human motions
References Axes
Longitudinal Axis
imaginary line around which TRANVERSE plane rotations occur
Anteroposterior Axis
imaginary line around which FRONTAL plane rotations occur
Mediolateral Axis
imaginary line around which SAGITTAL plane rotations occur
Reference Planes
Tranverse
rotational movement occur
Frontal
lateral movement occur
Sagittal
Foward and backward movements occur
Anatomical References Planes
Cardial Planes
Three imaginary perpendicular reference planes that divide body into half
Planes
Two dimensional surface with an orientation