a Red soni 3 éve
204
CHAPTER 6 PART 2
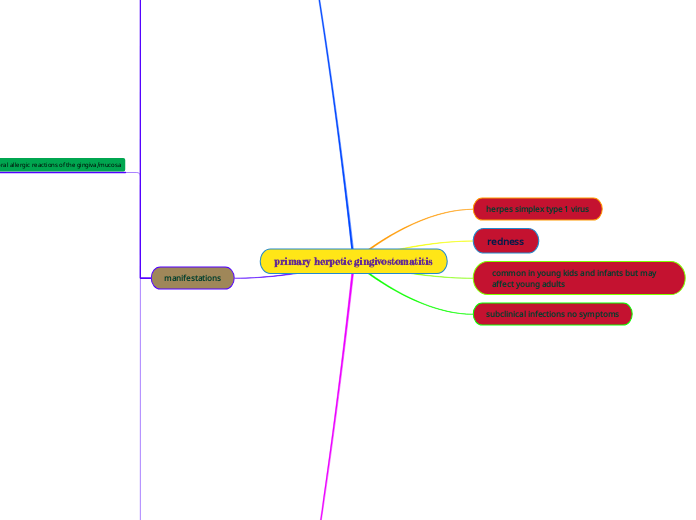
Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis is characterized by symptoms like fiery red marginal gingiva, yellowish ulcers with red halos, swollen lymph nodes, and papillae that bleed easily.
a Red soni 3 éve
204

Még több ilyen
Physical/mechanical insults
Gingival Pimentation
Amalgam tatoo
Drug induced pigmentation
Minocycline
Antimalarials
Smoker's melanosis
Melanoplakia
Chemical insults
burns
chemical insults
paraformaldehyde or calcium hydroxide
Dentifrice detergents
Hydrogen peroxide
Cocaine
Acetylsalicylic acid(asprin)
Chlorhexidine
Etching
factitious injury (self -harm)
Toothbrushing induced gingival ulceration
Frictional keratosis
malignant
Lymphoma
Leukemia
squamous cell carcinoma
premalignant
Erythroplakia
Leukoplakia
peripheral giant cell granuloma
pyogenic granuloma
calcifying fibroblastic granuloma
fibrous epulis
raised white lesions
ulceration
redness on gingiva
can last many years
cause unknown
lacy white patches
characterized by purplish itchy,swollen rash on skin
skin ad mucous membranes
crust formation on lower lip
blisters and ulcer on oral mucous membrane
large symmetrical red blotches
due to allergic reaction or infection
disorder of the skin and mucous membranes
tissue sloughing of mucosa
most common in those with history of other allergies