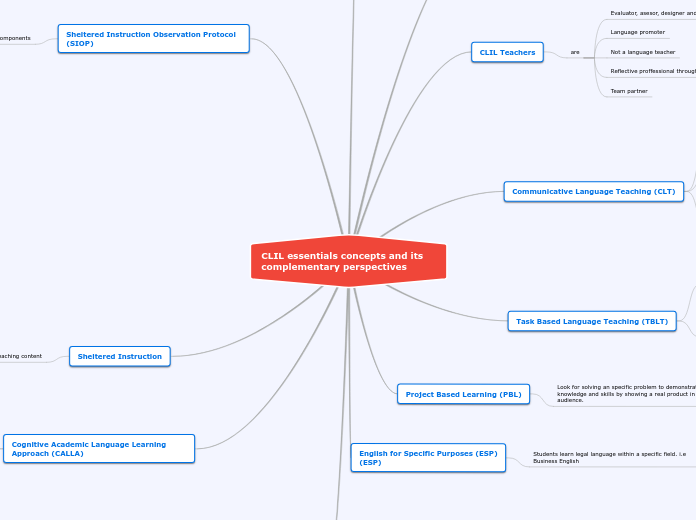
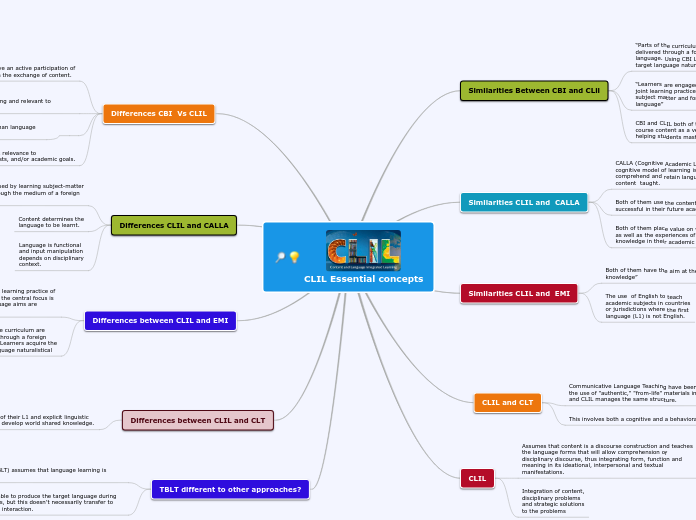
CLIL essentials concepts and its complementary perspectives
Content Based Instruction (CBI)
CBI curriculum
Appropiate to the need of specific groups of students
Uses authentic language text
Based on a subject matter core
Learning language through the study of subject matter
Cognitive Academic Language Learning Approach (CALLA)
Embody
Socio-affective strategies
Cognitive strategies
Metacognitive strategies
Student development of learning strategies
Instructional model developed for content and language learning
Sheltered Instruction
Teaching content
Socio-cultural awareness
Integration of meaningful language and content
English learners or native speakers English learners
Sheltered Instruction Observation Protocol (SIOP)
Based on 8 components
Lesson delivery
Create a lesson according to the students abilities
Students' engagement 90-100% of the lesson.
Content and language objectives
Review and assessment
Conduct assessment
Feedback
Review of key vocabulary
Practice and application
Integration of all language skills
Activities to apply content and language knowledge
Material
Interaction
Clarify concepts in L1
Group work helps with objectives
Create discussion
Strategies
Variety of question types
Scaffolding techniques per lesson
Variety of strategies
Comprehensible Input
Variation of techniques to clarify content concepts
Academic task
Appropriate use of speaking
Building Background
Key vocabulary
Differenciate past and new concepts
Linking concepts
Preparation
Choose concepts according to the age and the educational background
Define content and language objectives
English for Specific Purposes (ESP)
(ESP)
Students learn legal language within a specific field. i.e Business English
Project Based Learning (PBL)
Look for solving an specific problem to demonstrate their knowledge and skills by showing a real product in front of an audience.
Task Based Language Teaching (TBLT)
Tasks' assessment
Task completion
Solving communication problems
Meaning
Task is the core of language teaching.
Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)
Promotes
Autonomy
Fluency and accuracy
Active participation by students
Focused on
Organizational and pragmatical components
Real context
Teaching language for communication. (Harmer, 2012)
Improve the communicative skills in students
CLIL Teachers
are
Team partner
Reflective proffessional through the experiences
Not a language teacher
Language promoter
Evaluator, asesor, designer and planner
Hard CLIL
It is when language and content is taught at the same time
Soft CLIL
It is when a language learning is taught with a content