a ALEXANDRA SANTACRUZ 5 éve
189
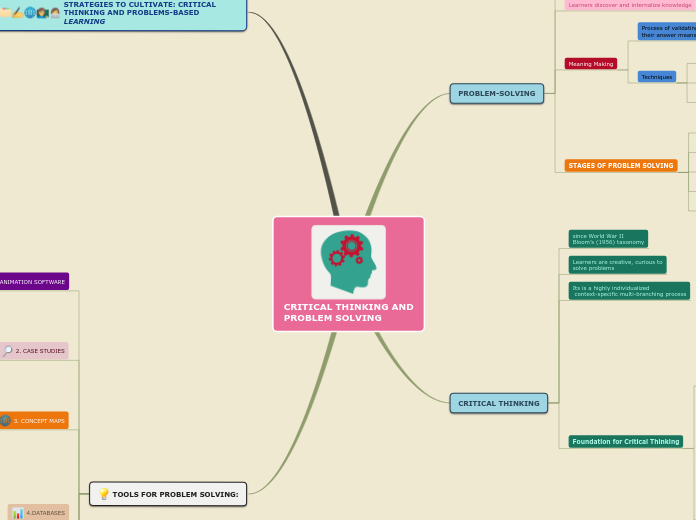
CRITICAL THINKING AND PROBLEM SOLVING
The use of various tools and methods significantly enhances critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Databases allow for the organization and management of extensive information, fostering new perspectives and aiding in report writing.