a SOFIA RHIANNA MONTENEGRO UTRERAS 1 éve
99
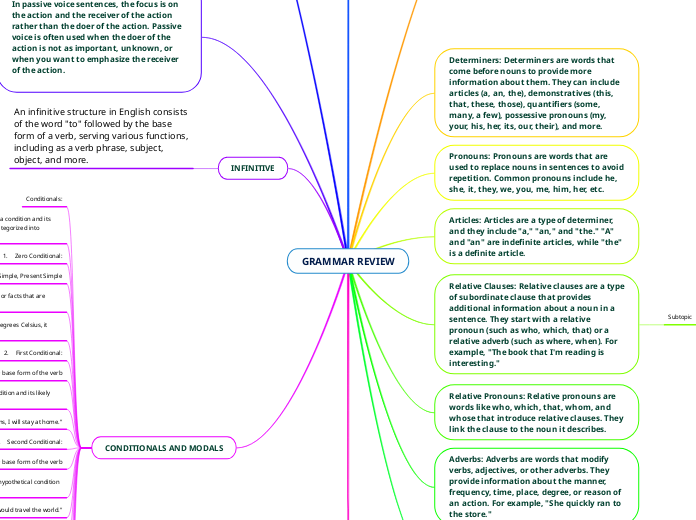
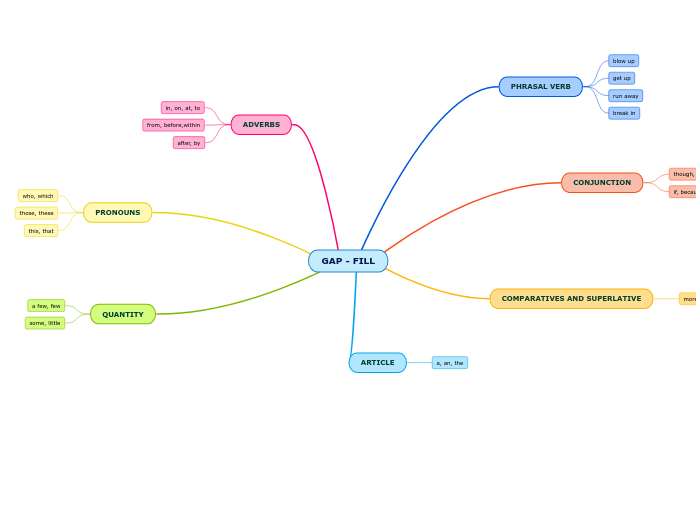
GRAMMAR REVIEW
Pronouns are utilized in sentences to replace nouns and avoid redundancy. Passive voice shifts the focus to the action or its receiver rather than the doer, and is useful when the doer is either unimportant or unknown.