a Juana Romero 9 éve
555
Hemodynamic Terminology
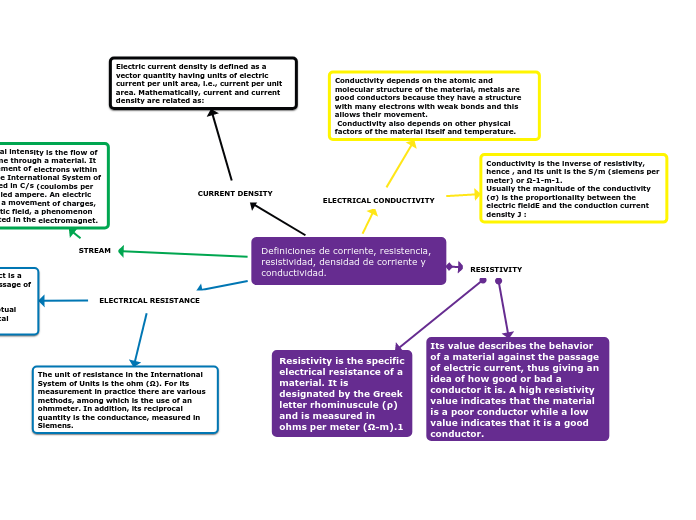
The concepts of hemodynamics involve understanding various parameters that influence heart function and blood circulation. Key measures include cardiac output, which is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute, and cardiac index, which adjusts this volume based on body surface area.