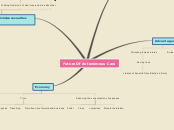
How did colonial rule impact the change in the social structure of India?
Was the new structure a reason for Indian nationalism?
Effects on the social structure
new classes
modern proletariate
working class (working in the new factories)
mainly impoverished peasants and artisans
modern bourgeoisie
landlords
industrialists
Villages
Caste panchayats lose their legal control
Village panchayats lose their legal control
New classes emerge
new class of money lenders
new class of merchants
Proprietor peasants
Absentee landlords
Zamindar
Land becomes a commodity
sell, buy, collateral
Changes due to Colonial rule
Cultural
modern press
modern english education
free of caste, gender considerations
Political
India councils act, 1861
representation of Indians in services
Administrative
New justice system
Civil/criminal courts
Criminal procedure code
Economic
Single currency
rail transport system
new industries
jute, steel, cotton mills
new land revenue system
Pre-British India
Cities
limited market since village is impenetrable
Classes mainly serve the upper classes and aristocracy
mainly populated by aristocrats, artisans, knowledge, military classes
Village
self sufficient system
absence of cash transactions
artisans, workmen- servants of village
peasants -leasers for generations
common land
Simple unchangeable asiatic societies- Karl Marx
Village republics- Charles Metcalfe