Retrieval
Consolidation
Encoding
Important studies
Important titles of theories/ideas
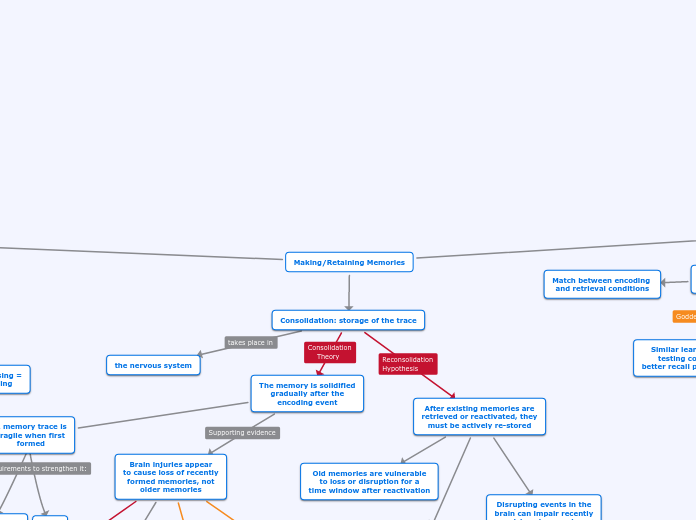
Making/Retaining Memories
3. Retrieval: recalling/reactivating the trace
False Memory
Retrieval process
has a period where
the information is
subject to influence
Your memory can
be manipulated
Repeated interviews
and discussions, & features of how they
are conducted, can cause a false memory to form
Trustworthy,
authoritative rapport
between interviewer
and participant
Guided
imagery
Social pressure to
retrieve memory
"Incontrovertible
eyewitness testimonies"
presented
Asking participants to
generate details for
fake memories increases
their "recall" of the
fake memory
Forgetting
Memory is fragile
at encoding, but
becomes stronger
with time & rehearsal
Older memories are
more difficult to
retrieve because
there is competition
from other memories
New information
can interfere with
retrieval
New memories
interfere with
remembering
old information
Old memories
interfere with
learning new
information
Passage of time
erodes memory
traces after encoding
Cues
More cues allow
for better recall
Transfer-appropriate
processing effect
Match between encoding
and retrieval conditions
Similar learning and
testing context =
better recall performance
2. Consolidation: storage of the trace
After existing memories are
retrieved or reactivated, they
must be actively re-stored
Disrupting events in the
brain can impair recently
retrieved memories
Episodic memory for details
of an emotional story
is worse in those who
underwent ECT immediately
after reading the story than in
those who did not get shocked
By disrupting the activity in the
amygdala(blocking protein
synthesis/structural changes),
this could stop reconsolidation
of the fearful memory
Antibiotic injected into rats'
amygdala immediately after
one trial of fear conditioning;
when presented with CS, much
less CR shown in groups given
high doses of antibiotic
The act of retrieving
a memory brings it
back to a fragile state
Old memories are vulnerable
to loss or disruption for a
time window after reactivation
The memory is solidified
gradually after the
encoding event
Brain injuries appear
to cause loss of recently
formed memories, not
older memories
ECT + TV show
knowledge
Selective loss of more
recent TV shows
after receiving shock
Rats trained to run
a maze, then given
a shock to the head
Time window between
completion of training
and administration of
shock varied among groups
Better maze learning
Poorer maze learning
Head trauma may disrupt
time-sensitive changes in
the nervous system
A pattern of memory
loss observed after
head trauma
There exists a brief
period of time before
the head injury that
the person cannot
remember
A memory trace is
fragile when first
formed
Changes in the
nervous system
Time
the nervous system
1. Encoding: creating the trace
Depth of Processing
Deeper processing =
better encoding
Shallow, Intermediate,
and Deep Groups
Greatest retention
in Deep, least
retention in Shallow
Meaning of the words is
considered more in
Deep than in Shallow
Associations to
Existing Memories
If the related information
precedes the target
information, then...
Related information
can enhance recall
Conscious Attention
Exposure alone
is not enough