a Lizzet Yasmin 4 éve
452
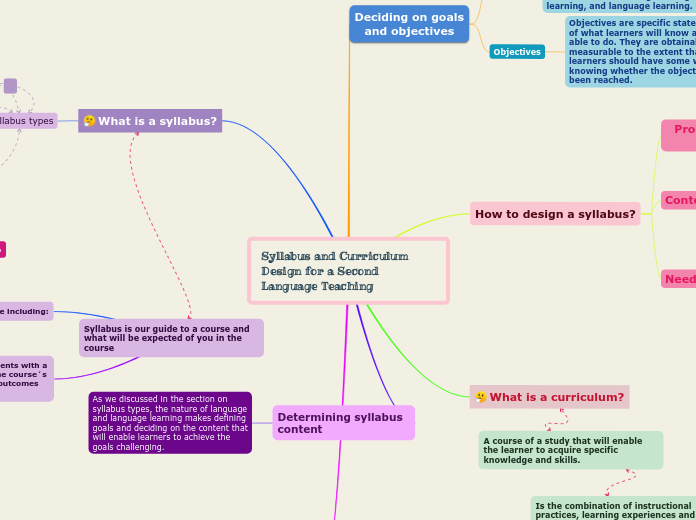
Syllabus and Curriculum Design for a Second Language Teaching
Developing an effective syllabus and curriculum for second language teaching is a multifaceted process that focuses on several key elements. Initially, a thorough context analysis is conducted to identify resources, constraints, and various influencing factors such as human resources, physical resources, and socio-cultural dynamics.