a jacob jennings 3 éve
141
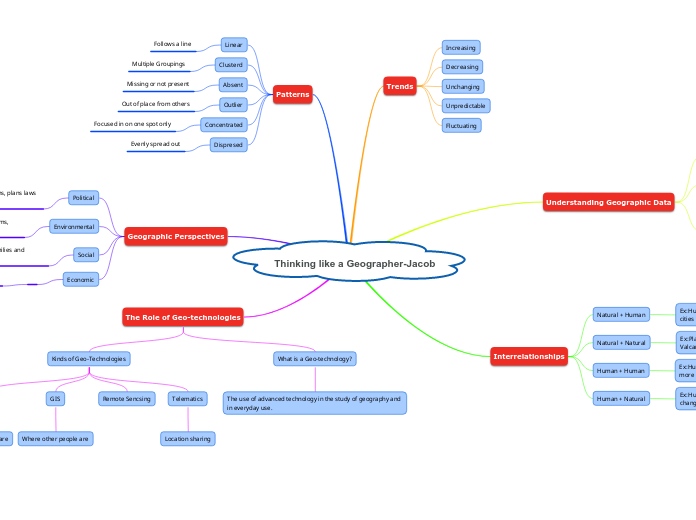
Thinking like a Geographer-Jacob
The integration of advanced technology in geography, known as geo-technologies, plays a pivotal role in both academic study and practical everyday applications. These technologies include tools like GPS, telematics, remote sensing, and GIS, each serving different purposes such as location sharing and identifying where people are.