da Isaac Garel mancano 4 anni
842
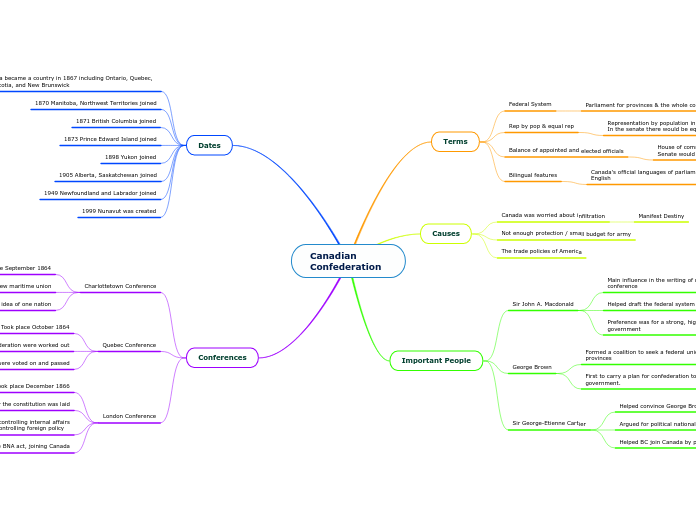
Canadian Confederation
In the mid-19th century, a series of pivotal conferences and influential figures laid the groundwork for what would become the Canadian Confederation. The Charlottetown, Quebec, and London Conferences played integral roles in shaping the new nation.