da Ivan Castillo manca 1 anno
102
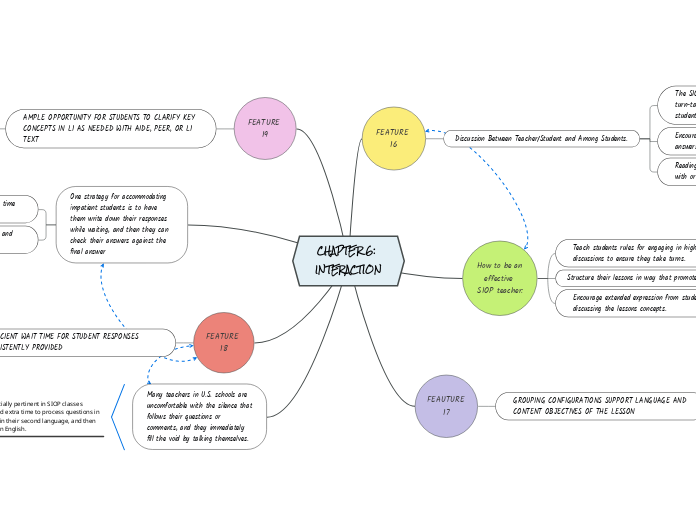
CHAPTER 6: INTERACTION
Transitioning from whole class to smaller group configurations and individual assignments enhances student collaboration and comprehension. This approach allows students to critique, analyze, and summarize material more effectively.