Clasificación de los trastornos de la niñez y la adolescencia
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
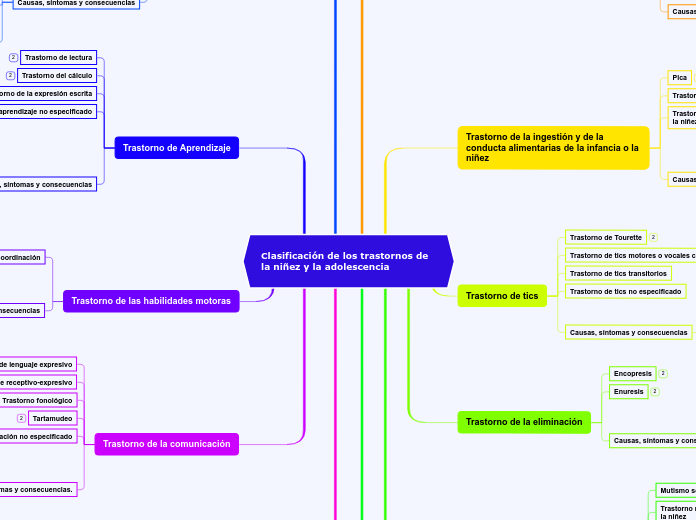
Trastorno generalizado del desarrollo
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Se observan en otras enfermedades medicas: anormalidades cronológicas, infecciones congénitas, anormalidades estructurales del sistema nervioso
Trastorno de Asperger
Trastorno de Rett
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
Trastorno autista
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
This stew is savory and delicious.
Trastorno de la comunicación
A preposition is one of the most exciting parts of grammar. A preposition is used to describe the location of something in relation to something else.
Causas, sintomas y consecuencias.
Dificultad para la adquisición de palabras nuevas y comprender palabras o frases, pueden estar asociados el déficit sensorial o motor del habla o privación ambiental de las deficiencias del lenguaje.
Interfiere en el rendimiento académico, comunicación social y laboral
Trastorno de la comunicación no especificado
A group of words used with the force of a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
according to, by means of, owing to, with a view to, in place of, in front of, etc.
Tartamudeo
Participle preposition consists of words that end in “ing”.
regarding, barring, concerning, considering, etc.
Trastorno fonológico
When a preposition consists of more than one word, it is called double preposition.
into, within, upto etc.
Trastorno mixto de lenguaje receptivo-expresivo
Compound preposition consists of two or more words.
on behalf of, according to, in front of, from across, etc.
Trastorno de lenguaje expresivo
When a preposition consists of one word it is called single or simple preposition.
in, at, on, to for, of, from, up, after, over, under, with, etc.
Trastorno de las habilidades motoras
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
Los sujetos asociados pueden caerse, chocar con los objetos, golpearlos como también interfiere en su rendimiento académico.
El diagnostico se establece si las deficiencias de la coordinación se deben a una enfermedad medica: parálisis cerebral, hemiplejia o distrofia muscular.
Trastorno del desarrollo de la coordinación
Trastorno de Aprendizaje
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
Rendimiento académico bajo, visión o audición alteradas y retraso mental.
Los trastornos de aprendizaje puede asociarse a desmoralización, baja autoestima, y déficit en habilidades sociales y al desarrollo de la coordinación.
Los problemas de aprendizaje interfieren significativamente el rendimiento académico las actividades de la vida cotidiana que requieren cálculo, lectura o escritura.
Trastorno del aprendizaje no especificado
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
down-toners
Fairly, Rather
intensifiers
Extremely, Very
Trastorno de la expresión escrita
Just, Afterward, Soon, Currently
Trastorno del cálculo
Always, usually, Never
Trastorno de lectura
Carefully, Slowly
Retraso Mental
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
La ausencia de habilidades para la comunicación puede predisponer a comportamientos agresivos y perturbadores
Sufrir abusos físicos y sexuales o a ver negados sus derechos y oportunidades.
Esta asociado al traumatismo craneal
Retraso mental moderado
Retraso mental grave
Retraso mental Profundo
Retraso mental de gravedad no especificada
Retraso mental leve
First, second..
Topic principal
Trastorno de ansiedad por separación
An article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Technically, an article is an adjective, which is any word that modifies a noun.
Los sujetos con este trastorno experimentan malestar excesivo al estar separados de su hogar o de las personas con quienes están vinculados. Algunos sujetos se muestran nostálgicos y desasosegados, preocupación. la alteración provoca malestar clínicamente significativo o deterioro social y académico
Trastorno desintegrativo infantil
Trastorno de movimientos estereotipados
Trastorno reactivo de la vinculación de la infancia o la niñez
Indefinite articles are the words 'a' and 'an.' Each of these articles is used to refer to a noun, but the noun being referred to is not a specific person, place, object, or idea. It can be any noun from a group of nouns.
A car in the parking lot.
Mutismo selectivo
It refers directly to a specific noun or groups of nouns.
The breakfast on my plate.
Trastorno de la eliminación
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Evacuación repetida de heces, emisión repetida de orina en la cama o en los vestidos.
Se debe a los efectos fisiológicos de una sustancia, también depende de la limitación ejercida sobre las actividades sociales del niño, nacimiento de un hermano, entrar a la escuela.
Enuresis
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
His, Your
Encopresis
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
He, They
Trastorno de tics
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Todas las formas de tics pueden asociarse por estrés y atenuarse durante actividades absorbentes, el trastorno provoca un notable malestar o deterioro significativo social, laboral o de otras áreas de actividad del individuo. el inicio es anterior a los 18 años de edad.
Trastorno de tics no especificado
Trastorno de tics transitorios
Trastorno de tics motores o vocales cronológicos
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
She is the prettiest princess.
Trastorno de Tourette
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
He is taller than she is.
Trastorno de la ingestión y de la conducta alimentarias de la infancia o la niñez
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Causas, síntomas y consecuencia
Produce aumento o perdida de pesos generando enfermedades como gastrointestinal endocrinóloga o neurológica.
Ingestión persistente de sustancias no nutritivas durante un periodo de por lo menos un mes. los sujetos se muestran generalmente irritables y hambrientos, pueden parecer apáticos y retraídos y experimentar retrasos del desarrollo.
Trastorno de la ingestión alimentaria de la infancia o la niñez
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Family, Class
Trastorno de Rumiación
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Cats, Rain
Pica
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Mary, Paris
Trastorno por déficit de atención y comportamiento perturbador
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Causas, síntomas y consecuencias
Los sujetos afectados de este trastornos pueden no prestar atención suficiente a los detalles o cometer errores por descuido en sus diferentes actividades, parecen tener su mente en otro lugar, evitan experimentan un fuerte disgusto hacia actividades que exigen una dedicación personal y un esfuerzo mental sostenido
Debe haber pruebas claras de interferencia en la actividad social o laboral propia del nivel de desarrollo.
Trastorno de comportamiento perturbador no especificado
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
The winning athlete gets a trophy.
Trastorno negativista desafiante
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
I might go to the park if I get my homework done.
Trastorno por déficit de atención con hiperactividad no especificado
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
You look exhausted after studying all night.
Trastorno por déficit de atención con hiperactividad
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
Create sentences
They have it.