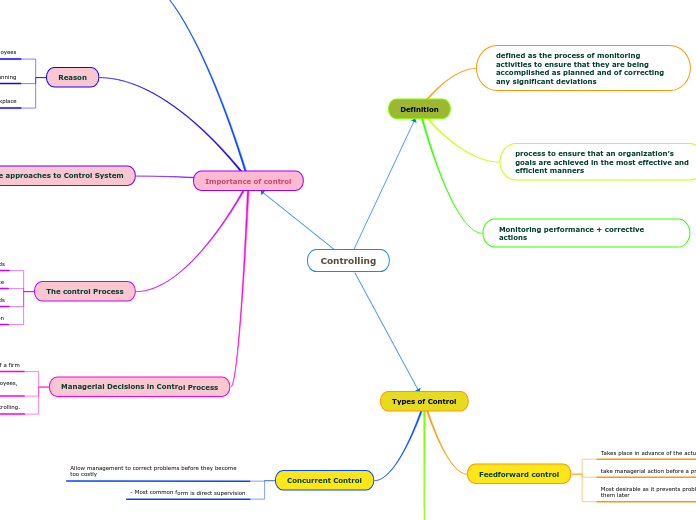
Definition
Monitoring performance + corrective actions
process to ensure that an organization’s goals are achieved in the most effective and efficient manners
defined as the process of monitoring activities to ensure that they are being accomplished as planned and of correcting any significant deviations
Types of Control
Concurrent Control
- Most common form is direct supervision
Allow management to correct problems before they become too costly
Feedback Control
Major drawback is that the damage is already done by the time the manager received the information
enhance employee motivation as it provides feedback to employees on their performance
provides meaningful information on how effective its planning effort was and can be used in future planning
Feedforward control
Most desirable as it prevents problems rather than to cure them later
take managerial action before a problem occurs
Takes place in advance of the actual activity
Importance of control
Managerial Decisions in Control Process
planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling.
include setting target growth rates, hiring or firing employees, and deciding what products to sell
Any decision regarding the operations of a firm
The control Process
4. Take Necessary Action
3. Compare actual performance with objectives and standards
2. Measure actual performance
1. Establishing performance objective and standards
Three approaches to Control System
Clan Control
Regulates behavior by shared values, norms, traditions, rituals, and beliefs of the firm’s culture.
eg, China: No 4 o’clock meetings , Japan: Keep an origami frog in your wallet
Bureaucratic Control
organizational authority and relies on rules, regulations, procedures, and policies.
- eg MOM, MOE, MOF
Market Control
Emphasizes the use of external market mechanisms to establish the standards used in the control system.
- eg, apple vs samsung, gojek vs grab vs taxis
Reason
Protecting workplace
Controls enhance physical security and help minimize workplace disruption
let managers know whether goals and plans are on target and what future actions to take
Empowering employees
Provide manager with information and feedback on employee performance
The planning-control link
Standard Measurements, Comparison, Actions
Leading
Motivation, Leadership, Communication, Individual and Group Behavior
Organizing
Structure, Human Resource Management
Planning
Goals, Objectives, Strategies, Plans
Controlling