DELITOS CONTRA LA ADMINISTRACIÓN DE JUSTICIA
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
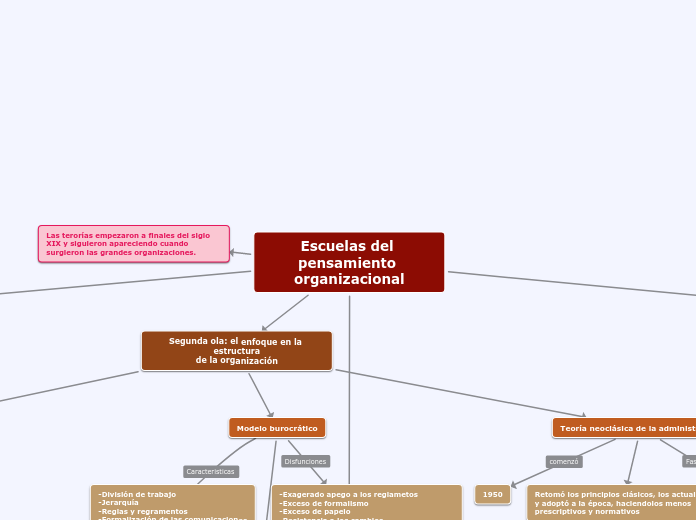
LA ADMINISTRACION DE JUSTICIA COMO BIEN JURIDICO AUTONOMO
Desde el punto de vista criminólogo donde los jueces venden sus decisiones desprestigiando al sistema y creando sentimientos de desconfianza en general
Los delitos contra la administración pública protegen el correcto ejercicio de la función publica en general y los delitos contra la administración de justicia pretenden tutelar el correcto funcionamiento de la Administración de Justicia
A preposition is one of the most exciting parts of grammar. A preposition is used to describe the location of something in relation to something else.
Phrase
A group of words used with the force of a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
according to, by means of, owing to, with a view to, in place of, in front of, etc.
Participle
Participle preposition consists of words that end in “ing”.
regarding, barring, concerning, considering, etc.
Double
When a preposition consists of more than one word, it is called double preposition.
into, within, upto etc.
Compound preposition consists of two or more words.
on behalf of, according to, in front of, from across, etc.
Simple
When a preposition consists of one word it is called single or simple preposition.
in, at, on, to for, of, from, up, after, over, under, with, etc.
DELITOS CONTRA LA ADMINISTRACION DE JUSTICIA
Sección I DELITOS CONTRA LA FUNCIÓN JURISDICCIONAL
Sección II PREVARICATO
Sección III DENEGACION Y RETARDO DE JUSTICIA
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
Other examples
"Woah!" or "Oops!"
PREVARICATO “El Juez o el Fiscal que dicta resolución o emite dictamen, manifiestamente contrarios al texto expreso y claro de la ley, o cita pruebas inexistentes o hechos falsos, o se apoya en leyes supuestas o derogadas…
Bien jurídico protegido Éste delito atenta contra la administración de justicia De la actuación infiel de los que integran los órganos jurisdiccionales o los ministerios públicos o de quienes intervienen en ellos como auxiliares
erb
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
Focusing Adverbs
Especially, Specifically, Merely, Either
Adverbs of Quantity
A lot, Little, Much
Adverbs of Degree
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
down-toners
Fairly, Rather
intensifiers
Extremely, Very
Adverbs of Relative Time
Just, Afterward, Soon, Currently
Adverbs of Frequency
Always, usually, Never
Adverbs of Manner
Carefully, Slowly
“Artículo 407.- Omisión de denuncia
El que omite comunicar a la autoridad las noticias que tenga acerca de la comisión de algún delito, cuando esté obligado a hacerlo por su profesión o empleo, será reprimido con pena privativa de libertad no mayor de dos años.
Si el hecho punible no denunciado tiene señalado en la ley pena privativa de libertad superior a cinco años, la pena será no menor de dos ni mayor de cuatro años.
Si la omisión está referida a los delitos de genocidio, tortura o desaparición forzada, la pena será no menor de dos ni mayor de seis años ”.
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
Cardinal numbers
One, two..
Ordinal numbers
First, second..
Excusa absolutoria
Artículo 406.- Están exentos de pena los que ejecutan cualquiera de los hechos previstos en los artículos 404º y 405º si sus relaciones con la persona favorecida son tan estrechas como para excusar su conducta.
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
Compound
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
Candlestick
Collective
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Family, Class
Countable/Uncountable
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Cats, Rain
Proper/Common
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
Mary, Paris
EL BIEN JURIDICO PROTEGIDO
“EL bien jurídico protegido es el correcto funcionamiento de la administración de justicia, institución fundamental para la convivencia social y desarrollo de las libertades y otros principios democráticos de cualquier país” Serrano Gomez
El presente capitulo no protegido a la administración de Justicia como poder del estado, sino como servicio público hacia los ciudadanos; lo que interesa al Derecho penal, son aquellas actuaciones encaminadas a perturbar el correcto funcionamiento de la administración de justicia.
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Subordinating conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
Coordinating
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
This stew is savory and delicious.
402 DENUNCIA CALUMNIOSA
El que denuncia a la autoridad un hecho punible, a sabiendas que no se ha cometido, o el que simula pruebas o indicios de su comisión que pueden servir de motivo para un proceso penal o el que falsamente se atribuye delito no cometido o que ha sido cometido por otro, será reprimido con pena privativa de libertad no mayor de tres años.
"Cuando la simulación directa o indirecta de pruebas o indicios de su comisión sea efectuada por miembros de la Policía Nacional u otro funcionario o servidor público encargado de la prevención del delito, y que puedan servir de sustento para un proceso penal por tráfico ilícito de drogas , la pena privativa de libertad será no menor de tres ni mayor de seis años.
BIEN JURÍDICO PROTEGIDO: es la correcta administración de Justicia.
SUJETO ACTIVO: Cualquiera
SUJETO PASIVO: El estado
TIPO SUBJETIVO: Dolo
Delito de mera actividad
An article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Technically, an article is an adjective, which is any word that modifies a noun.
Subtopic
Indefinite article
Indefinite articles are the words 'a' and 'an.' Each of these articles is used to refer to a noun, but the noun being referred to is not a specific person, place, object, or idea. It can be any noun from a group of nouns.
A car in the parking lot.
Definite article
It refers directly to a specific noun or groups of nouns.
The breakfast on my plate.
403 OCULTAMIENTO DE MENOR A LAS INVESTIGACIONES
"El que oculta a un menor de edad a las investigaciones de la justicia o de la que realiza la autoridad competente, será reprimido con pena privativa de libertad no menor de uno ni mayor de tres años"
Sujeto activo: Cualquier persona
Sujeto pasivo: Es el Estado
Tipo Subjetivo: Requiere dolo
Delito de mera actividad no requiere la producción de un resultado en el sentido de que se llegue a obstaculizar los fines de la investigación, basta que tome lugar el acto de ocultamiento.
Delito de Consumación Instantanea, admite tentativa.
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Indefinite
Unlike demonstrative pronouns, which point out specific items, indefinite pronouns are used for non-specific things. This is the largest group of pronouns. All, some, any, several, anyone, nobody, each, both, few, either, none, one, and no one are the most common.
None, Several
Relative
Relative pronouns are used to add more information to a sentence. Which, that, who (including whom and whose), and where are all relative pronouns.
Which, Where
Interrogative
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
Which, Who
Reciprocal
Reciprocal pronouns are used for actions or feelings that are reciprocated. The reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Each other, one another
Reflexive
A reflexive pronoun ends with ...self or ...selves and refers to another noun or pronoun in the sentence (usually the subject of the sentence). The reflexive pronouns are myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Itself, Himself
Demonstrative
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
This, These
Possesive
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
His, Your
Personal
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
He, They
Artículo 404.- Encubrimiento personal
El que sustrae a una persona de la persecución penal oa la ejecución de una pena o de otra medida ordenada por la justicia, será reprimido con pena privativa de libertad no menor de tres ni mayor de seis años.
Si el Agente sustrae al autor de los delitos previstos en los artículos 152 al 153 A, 200, 273 al 279-D, 296 al 298, 315, 317, 318-A, 325 al 333; 346 al 350, en la Ley Nº 27765 (Ley Penal contra el Lavado de Activos) o en el Decreto Ley Nº 25475 (Establecen la penalidad para los delitos de terrorismo y los procedimientos para la investigación, la instrucción y el juicio), la pena privativa de libertad será no menor de siete ni mayor de diez años y de ciento ochenta a trescientos sesenticinco días-multa.
Si el autor del encubrimiento personal es funcionario o servidor público encargado de la investigación del delito o de la custodia del delincuente, la pena será privativa de libertad no menor de diez ni mayor de quince años ”.
Artículo 405.- El que dificulta la acción de la justicia procurando la desaparición de las huellas o prueba del delito u ocultando los efectos del mismo, será reprimido con pena privativa de libertad no menor de dos ni mayor de cuatro años.
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
Superlative
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
She is the prettiest princess.
Comparative
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
Create sentences
He is taller than she is.