Therefore by doing this lab we can confirm the existence of spinning electrons
The theoretical explination for his findings were that electrons orbit in quantized shells
and electrons within an atom can possess only certain discrete/distinct/unique energies called energy levels
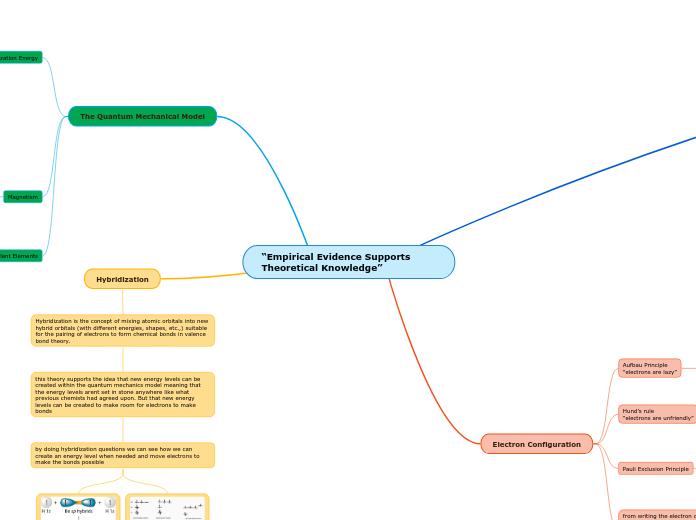
“Empirical Evidence Supports Theoretical Knowledge”
Hybridization
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc.,) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory.
this theory supports the idea that new energy levels can be created within the quantum mechanics model meaning that the energy levels arent set in stone anywhere like what previous chemists had agreed upon. But that new energy levels can be created to make room for electrons to make bonds
by doing hybridization questions we can see how we can create an energy level when needed and move electrons to make the bonds possible
The Quantum Mechanical Model
Multivalent Elements
Magnetism
The magnetism lab supports the idea of the electrons spinning in the quantum mechanics model
Elements that do have unpaired electrons can be affected by a magnetic field
Because there are unpaired electrons the opposite spins dont cancel out giving a net spin. This affects the entire atom and creates a magnetic moment
Unpaired electrons= net spin = Magnetic moment = attraction
Elements that dont have any unpaired electrons arent affected by a magnetic field
This is because the opposite spins cancel eachother out, making the total spin 0, cancelling out any magnetic moment and therefore cant be affected by a magnetic field
No unpaired electrons = No magnetic moment = no attraction
Ionization Energy
Looking that the ionization energies they decrease as we move down which also means our principle quantum # increases. This means the probable distance of the electron from the nucleus. In other words, it refers to the size of the orbital and the energy level an electron is placed in. Bigger principle quantum # means farther away from nucleus and means less hold on the valance electrons meaning easier to ionize
This supports the theory of how the quantum mechanical model behaves, meaning the probability of the eletctons and how its structured energy shell wise
Electron Configuration
from writing the electron configuration we can use all these theories to make the empirical evidence, these theories support the empirical evidence by making the 1s orbitals the lowest energy levels it also means it spends most of its time closer to the radius which matches up.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
If two electrons are in the same orbital (paired up), the two electrons will have opposite spin
Hund’s rule
“electrons are unfriendly”
Spread out electrons as much as possible in each subshell before pairing the electrons
Aufbau Principle
“electrons are lazy”
Assign electrons in increasing order starting at the lowest energy levels and building up
History of the Atom and the fundamental men that came up with major atomic models
Neils Bohr
From his observations he concluded that each element has its own unique line spectrum emmission
Neils Bohr was the first scientist to use the quantum theory to try to describe the model of an atom in that the electrons were limited to specific orbits around the nucleus.
Ernest Rutherford
He developed the nuclear model using the gold foil expirement
During his expirement he found some particles passed straight through while some deflected or bounced back
From that expirement he concluded that the theoretical explenation is that the atom is .....
most of the atoms mass is a positive core/ positive nucleus
electrons exist around the nucleus
mostly empty space
JJ Thompson
He developed the chocolate chip cookie model
JJ used some cathode ray tubes which showed that all atoms contain tiny negatively charged subatomic particles or electrons. Thomson knew that atoms had an overall neutral charge. Therefore, he reasoned that there must be a source of positive charge within the atom to counterbalance the negative charge on the electrons.
Thomson's chocolate chip cookie model of the atom had negatively-charged electrons embedded within a positively-charged "cookie dough".
From those expiriments he developed 2 major idea's based on his findings
1- negative particles exist in positive framework
2- elements are characterized by the number of electrons
John Dalton
He was one of the first scientists to use data to support his theories
John Dalton came out with the idea in 1805 that atoms are like billiard balls. He named it an atom because it comes from the greek word meaning not divisible. From there he came out with 3 laws.
Law of definite composition
a given chemical compound always contains its component elements in fixed ratio and does not depend on its source and method of preparation
Law of multiple proportions
The theoretical knowledge is that atoms of two or more elements can combine in constant ratios to form new substances.
Law of conservation of mass
The theoretical knowledge that supports this law is that In chemical reactions, atoms join together or separate from each other but are not destroyed.
The sum of the mass of all the reactants should equal the products
Aristotle and Demicritus
Democritus also came out with the idea that everything is made up of atoms and empty space (void) and that atoms are indivisible
The empirical evidence that democritus had on atoms even though he could not see them was if you took a block of matter, lets say a block of cheese, if you cut it up enough times you would reach a point were it couldn't be divided any more and then you would be left with an atom.
Aristotle came out with the proposed idea that 4 elements make up our entire world; air, fire, earth and water.
The empirical evidence that Aristotle had to prove this was what he saw with his observations in the procedures that he did and what he saw.
Fire and air made objects hot, water and earth made objects cold and so on