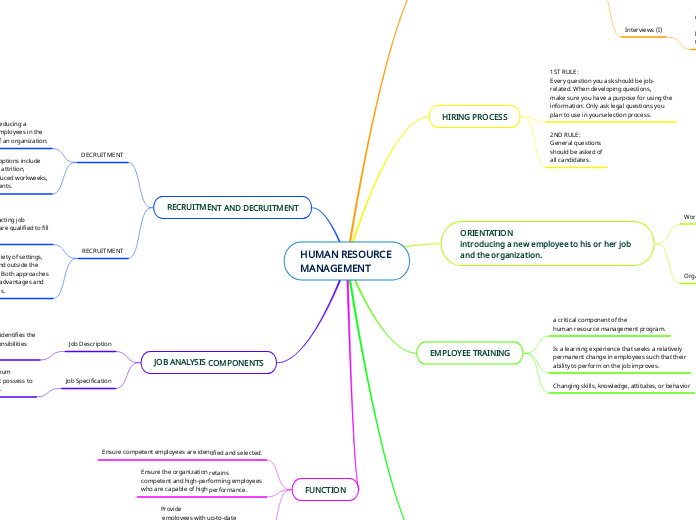
HUMAN RESOURCE
MANAGEMENT
FUNCTION
Provide
employees with up-to-date
knowledge and skills to do their jobs.
Ensure the organization retains
competent and high-performing employees
who are capable of high performance.
Ensure competent employees are identified and selected.
JOB ANALYSIS COMPONENTS
Job Specification
A written statement of the minimum
qualifications that a person must possess to
perform a given job successfully.
Job Description
Job description identifies the
tasks and responsibilities
of a position.
RECRUITMENT AND DECRUITMENT
RECRUITMENT
occur in a variety of settings,
both inside and outside the
organization. Both approaches
have certain advantages and
disadvantages.
process of
finding and attracting job
candidates who are qualified to fill
job vacancies
DECRUITMENT
Decruitment options include
firing, layoffs, attrition,
transfers, reduced workweeks,
early retirements.
process of reducing a
surplus of employees in the
workforce of an organization.
THE IMPORTANCE OF HUMAN
RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM)
Adds value to the firm
High performance work practices lead to both high
individual and high organizational performance.
As an important strategic tool
HRM helps establish an organization’s sustainable
competitive advantage.
As a necessary part of the organizing
function of management
Evaluating the work force
Training
Selecting
EMPLOYEE TRAINING
Changing skills, knowledge, attitudes, or behavior
Is a learning experience that seeks a relatively
permanent change in employees such that their
ability to perform on the job improves.
a critical component of the
human resource management program.
ORIENTATION
introducing a new employee to his or her job and the organization.
Organization orientation
Includes a tour of the entire facility
Informs new employee about the organization’s objectives, history, philosophy, procedures, and rules.
Work-unit orientation.
Introduces he or she to his or her coworkers
Clarifies how his or her job contributes to unit goals
Familiarizes new employee with work-unit goals
HIRING PROCESS
2ND RULE:
General questions
should be asked of
all candidates.
1ST RULE:
Every question you ask should be job-
related. When developing questions,
make sure you have a purpose for using the
information. Only ask legal questions you
plan to use in yourselection process.
SELECTION
SELECTION DEVICES
Interviews (I)
relatively formal, in-depth conversations
conducted for the purpose of assessing a candidate’s knowledge, skills, and abilities, as well as providing information to the candidate about the organization and potential jobs.
Realistic job preview (RJP)
devices used in the early stages of employees’ selection to provide
potential applicants with information on both positive and negative aspects of the job (Premack & Wanous, 1985).
Performance-simulation tests (PST)
Performance tests consist of actual job
behaviors -Testing an applicant’s ability to
perform actual job behaviors, use required
Written tests (WT)
test knowledge, ability, skill, intelligence, or interest.
The process of screening job applicants to ensure
that the most appropriate candidates are hired.